A tandem-repeat dimeric RBD protein-based covid-19 vaccine zf2001 protects mice and nonhuman primates
- PMID: 35311493
- PMCID: PMC9009945
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2056524
A tandem-repeat dimeric RBD protein-based covid-19 vaccine zf2001 protects mice and nonhuman primates
Abstract
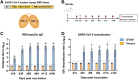
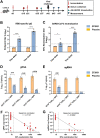
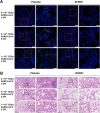
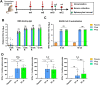
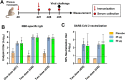
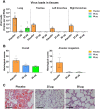
Safe, efficacious, and deployable vaccines are urgently needed to control COVID-19 in the large-scale vaccination campaigns. We report here the preclinical studies of an approved protein subunit vaccine against COVID-19, ZF2001, which contains tandem-repeat dimeric receptor-binding domain (RBD) protein with alum-based adjuvant. We assessed vaccine immunogenicity and efficacy in both mice and non-human primates (NHPs). ZF2001 induced high levels of RBD-binding and SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody in both mice and non-human primates, and elicited balanced TH1/TH2 cellular responses in NHPs. Two doses of ZF2001 protected Ad-hACE2-transduced mice against SARS-CoV-2 infection, as detected by reduced viral RNA and relieved lung injuries. In NHPs, vaccination of either 25 μg or 50 μg ZF2001 prevented infection with SARS-CoV-2 in lung, trachea, and bronchi, with milder lung lesions. No evidence of disease enhancement was observed in both animal models. ZF2001 has been approved for emergency use in China, Uzbekistan, Indonesia, and Columbia. The high safety, immunogenicity, and protection efficacy in both mice and NHPs found in this preclinical study was consistent with the results in human clinical trials.
Keywords: Covid-19; antibody; immune response; subunit protein vaccine; zf2001.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/.
-
- Li J, Lai S, Gao GF, et al. . The emergence, genomic diversity and global spread of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. 2021. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
