Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs
- PMID: 35311495
- PMCID: PMC8942545
- DOI: 10.1080/19932820.2022.2054111
Effects of vitamin C and D on the mRNA expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor, cathepsin L, and transmembrane serine protease in the mouse lungs
Abstract
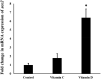
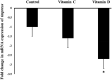
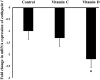
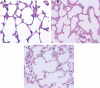
Vitamins (Vit) C and D are widely used as immunogenic supplements among severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infected patients. The SAR-CoV-2 virus enters into the pulmonary endothelial cells through attachment to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor (Ace2) and the proteolytic activity of Cathepsin L (Ctsl) and transmembrane serine protease 2 (Tmprss2) enzymes. This study aimed to determine the influence of Vit C and D on the mRNA expression of Ace2, Tmprss2, and Ctsl genes in the mouse lungs. Vitamins C and D were administrated to different groups of mice through intra-peritoneal route in doses equivalent to human for 30 days. Then, the mRNA expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry gene was analyzed using qRT-PCR. It is found that Vit D, but not C, upregulated significantly (P < 0.05) the mRNA expression of Ace2 by more than six folds, while downregulated the expression of Ctsl and Tmprss2 genes by 2.8 and 2.2 folds, respectively. It can be concluded from this study that Vit D alters the mRNA expression of Ace2, Tmprss, and Ctsl genes in the mouse lungs. This finding can help us in understanding, at least in part, the molecular influence of Vit D on genes involved in the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells.
Keywords: Ace2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; lungs; vitamin C; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations in the gene expression of SARS-COV-2 entry receptors and enzymes in lungs and hearts of controlled and uncontrolled diabetic mice.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;38(2):328-340. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12964. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37950353
-
Human eggs, zygotes, and embryos express the receptor angiotensin 1-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane serine protease 2 protein necessary for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.F S Sci. 2021 Feb;2(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.xfss.2020.12.005. Epub 2020 Dec 24. F S Sci. 2021. PMID: 33521687 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling meta-analysis of ACE2 and TMPRSS2, the putative anti-inflammatory receptor and priming protease of SARS-CoV-2 in human cells, and identification of putative modulators.Redox Biol. 2020 Sep;36:101615. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101615. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 32863223 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin L, transmembrane peptidase/serine subfamily member 2/4, and other host proteases in COVID-19 pathogenesis - with impact on gastrointestinal tract.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Oct 21;27(39):6590-6600. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i39.6590. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34754154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions of renin-angiotensin system and COVID-19: the importance of daily rhythms in ACE2, ADAM17 and TMPRSS2 expression.Physiol Res. 2021 Dec 16;70(S2):S177-S194. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934754. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34913351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Vitamin D and Resveratrol Performances in COVID-19.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 5;15(11):2639. doi: 10.3390/nu15112639. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Zinc, Vitamins C and D on Disease Prognosis among Patients with COVID-19 in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 26;14(23):5029. doi: 10.3390/nu14235029. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501059 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Vitamin D Receptor Genotype on Lipid Profiles and Retinopathy Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Pilot Study.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 11;12(9):1488. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091488. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143273 Free PMC article.
-
rs12329760 Polymorphism in Transmembrane Serine Protease 2 Gene and Risk of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Mortality.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Nov 22;2022:7841969. doi: 10.1155/2022/7841969. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36457338 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
