Different Conformations Revealed by NMR Underlie Resistance to Ceftazidime/Avibactam and Susceptibility to Meropenem and Imipenem among D179Y Variants of KPC β-Lactamase
- PMID: 35311523
- PMCID: PMC9017342
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.02124-21
Different Conformations Revealed by NMR Underlie Resistance to Ceftazidime/Avibactam and Susceptibility to Meropenem and Imipenem among D179Y Variants of KPC β-Lactamase
Abstract
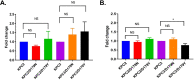
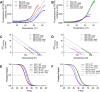
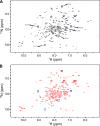
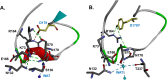
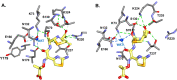
β-Lactamase-mediated resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam (CZA) is a serious limitation in the treatment of Gram-negative bacteria harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC). Herein, the basis of susceptibility to carbapenems and resistance to ceftazidime (CAZ) and CZA of the D179Y variant of KPC-2 and -3 was explored. First, we determined that resistance to CZA in a laboratory strain of Escherichia coli DH10B was not due to increased expression levels of the variant enzymes, as demonstrated by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). Using timed mass spectrometry, the D179Y variant formed prolonged acyl-enzyme complexes with imipenem (IMI) and meropenem (MEM) in KPC-2 and KPC-3, which could be detected up to 24 h, suggesting that IMI and MEM act as covalent β-lactamase inhibitors more than as substrates for D179Y KPC-2 and -3. This prolonged acyl-enzyme complex of IMI and MEM by D179Y variants was not observed with wild-type (WT) KPCs. CAZ was studied and the D179Y variants also formed acyl-enzyme complexes (1 to 2 h). Thermal denaturation and differential scanning fluorimetry showed that the tyrosine substitution at position 179 destabilized the KPC β-lactamases (KPC-2/3 melting temperature [Tm] of 54 to 55°C versus D179Y Tm of 47.5 to 51°C), and the D179Y protein was 3% disordered compared to KPC-2 at 318 K. Heteronuclear 1H/15N-heteronuclear single quantum coherence (HSQC) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy also revealed that the D179Y variant, compared to KPC-2, is partially disordered. Based upon these observations, we discuss the impact of disordering of the Ω loop as a consequence of the D179Y substitution. These conformational changes and disorder in the overall structure as a result of D179Y contribute to this unanticipated phenotype.
Keywords: D179Y; KPC; KPC D179Y; Klebsiella pneumoniae; antibiotic resistance; beta-lactamases; ceftazidime-avibactam resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare a conflict of interest. Dr. Bonomo reports grants from Entasis, Merck, Shionogi, and Venatorx.
Figures
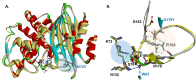
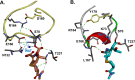
References
-
- Levitt PS, Papp-Wallace KM, Taracila MA, Hujer AM, Winkler ML, Smith KM, Xu Y, Harris ME, Bonomo RA. 2012. Exploring the role of a conserved class A residue in the omega-loop of KPC-2 beta-lactamase: a mechanism for ceftazidime hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 287:31783–31793. 10.1074/jbc.M112.348540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shields RK, Potoski BA, Haidar G, Hao B, Doi Y, Chen L, Press EG, Kreiswirth BN, Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH. 2016. Clinical outcomes, drug toxicity, and emergence of ceftazidime-avibactam resistance among patients treated for carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae infections. Clin Infect Dis 63:1615–1618. 10.1093/cid/ciw636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shields RK, Chen L, Cheng S, Chavda KD, Press EG, Snyder A, Pandey R, Doi Y, Kreiswirth BN, Nguyen MH, Clancy CJ. 2017. Emergence of ceftazidime-avibactam resistance due to plasmid-borne blaKPC-3 mutations during treatment of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e02097-16. 10.1128/AAC.02097-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

