The Value of Passive Leg Raise During Right Heart Catheterization in Diagnosing Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 35311526
- PMCID: PMC9009844
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008935
The Value of Passive Leg Raise During Right Heart Catheterization in Diagnosing Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Background: Because of limited accuracy of noninvasive tests, diastolic stress testing plays an important role in the diagnostic work-up of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Exercise right heart catheterization is considered the gold standard and indicated when HFpEF is suspected but left ventricular filling pressures at rest are normal. However, performing exercise during right heart catheterization is not universally available. Here, we examined whether pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) during a passive leg raise (PLR) could be used as simple and accurate method to diagnose or rule out occult-HFpEF.
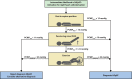
Methods: In our tertiary center for pulmonary hypertension and HFpEF, all patients who received a diagnostic right heart catheterization with PCWP-measurements at rest, PLR, and exercise were evaluated (2014-2020). The diagnostic value of PCWPPLR was compared with the gold standard (PCWPEXERCISE). Cut-offs derived from our cohort were subsequently validated in an external cohort (N=74).
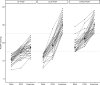
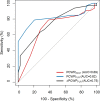
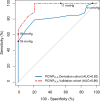
Results: Thirty-nine non-HFpEF, 33 occult-HFpEF, and 37 manifest-HFpEF patients were included (N=109). In patients with normal PCWPREST (<15 mmHg), PCWPPLR significantly improved diagnostic accuracy compared with PCWPREST (AUC=0.82 versus 0.69, P=0.03). PCWPPLR ≥19 mmHg (24% of cases) had a specificity of 100% for diagnosing occult-HFpEF, irrespective of diuretic use. PCWPPLR ≥11 mmHg had a 100% sensitivity and negative predictive value for diagnosing occult-HFpEF. Both cut-offs retained a 100% specificity and 100% sensitivity in the external cohort. Absolute change in PCWPPLR or V-wave derived parameters had no incremental value in diagnosing occult-HFpEF.
Conclusions: PCWPPLR is a simple and powerful tool that can help to diagnose or rule out occult-HFpEF.
Keywords: diuretic; heart failure; hypertension, pulmonary; leg; pulmonary wedge pressure.
Figures
Comment in
-
Passive Leg Raise: A Leg Up in the Diagnosis of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction?Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Apr;15(4):e009410. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.122.009410. Epub 2022 Mar 21. Circ Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35311506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lewis EF, Lamas GA, O’Meara E, Granger CB, Dunlap ME, McKelvie RS, Probstfield JL, Young JB, Michelson EL, Halling K, et al. ; CHARM Investigators. Characterization of health-related quality of life in heart failure patients with preserved versus low ejection fraction in CHARM. Eur J Heart Fail. 2007;9:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2006.10.012 - PubMed
-
- Obokata M, Kane GC, Reddy YN, Olson TP, Melenovsky V, Borlaug BA. Role of diastolic stress testing in the evaluation for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a simultaneous invasive-echocardiographic study. Circulation. 2017;135:825–838. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024822 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharifov OF, Gupta H. What is the evidence that the tissue doppler index E/e’ reflects left ventricular filling pressure changes after exercise or pharmacological intervention for evaluating diastolic function? A systematic review. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e004766. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.004766 - PMC - PubMed
-
- van de Bovenkamp AA, Enait V, de Man FS, Oosterveer FTP, Bogaard HJ, Vonk Noordegraaf A, van Rossum AC, Handoko ML. Validation of the 2016 ASE/EACVI guideline for diastolic dysfunction in patients with unexplained dyspnea and a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10:e021165. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.021165 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hummel YM, Liu LCY, Lam CSP, Fonseca-Munoz DF, Damman K, Rienstra M, van der Meer P, Rosenkranz S, van Veldhuisen DJ, Voors AA, et al. . Echocardiographic estimation of left ventricular and pulmonary pressures in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a study utilizing simultaneous echocardiography and invasive measurements. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19:1651–1660. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.957 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

