Transition of Dephospho-DctD to the Transcriptionally Active State via Interaction with Dephospho-IIAGlc
- PMID: 35311533
- PMCID: PMC9040800
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.03839-21
Transition of Dephospho-DctD to the Transcriptionally Active State via Interaction with Dephospho-IIAGlc
Abstract
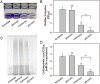
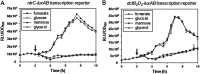
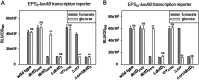
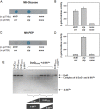
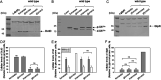
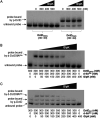
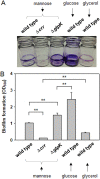
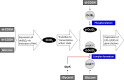
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs), biofilm-maturing components of Vibrio vulnificus, are abundantly produced when the expression of two major EPS gene clusters is activated by an enhancer-binding transcription factor, DctD2, whose expression and phosphorylation are induced by dicarboxylic acids. Surprisingly, when glucose was supplied to V. vulnificus, similar levels of expression of these clusters occurred, even in the absence of dicarboxylic acids. This glucose-dependent activation was also mediated by DctD2, whose expression was sequentially activated by the transcription regulator NtrC. Most DctD2 in cells grown without dicarboxylic acids was present in a dephosphorylated state, known as the transcriptionally inactive form. However, in the presence of glucose, a dephosphorylated component of the glucose-specific phosphotransferase system, d-IIAGlc, interacted with dephosphorylated DctD2 (d-DctD2). While d-DctD2 did not show any affinity to a DNA fragment containing the DctD-binding sequences, the complex of d-DctD2 and d-IIAGlc exhibited specific and efficient DNA binding, similar to the phosphorylated DctD2. The d-DctD2-mediated activation of the EPS gene clusters' expression was not fully achieved in cells grown with mannose. Furthermore, the degrees of expression of the clusters under glycerol were less than those under mannose. This was caused by an antagonistic and competitive effect of GlpK, whose expression was increased by glycerol, in forming a complex with d-DctD2 by d-IIAGlc. The data demonstrate a novel regulatory pathway for V. vulnificus EPS biosynthesis and biofilm maturation in the presence of glucose, which is mediated by d-DctD2 through its transition to the transcriptionally active state by interacting with available d-IIAGlc. IMPORTANCE Transcription regulation by bacterial two-component systems is achieved by a response regulator upon its transition to the transcriptionally active form via kinase activity of its cognate sensor under specific conditions. A well-known response regulator, DctD, is converted to its phosphorylated form when DctB senses ambient dicarboxylic acids. Phospho-DctD induces expression of its regulon, including the gene clusters for biosynthesis of exopolysaccharides (EPSs), the essential constituents of biofilm matrix. In the absence of dicarboxylic acids, however, DctD-mediated induction of these EPS gene clusters and biofilm maturation was observed if glucose was supplied. This suggests that dephospho-DctD could play a role in activating the transcription of target genes. A component of glucose-phosphotransferase system, IIAGlc, was present in a dephosphorylated state in the presence of glucose. Dephospho-DctD formed a complex with dephospho-IIAGlc and was converted to a transcriptionally active state. These findings suggest the other response regulators could also have alternative pathways of activation independent of phosphorylation.
Keywords: biofilm; dephospho-DctD; dephospho-IIAGlc; exopolysaccharides; glucose.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
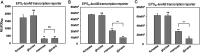

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the transcriptionally active form of dephosphorylated DctD complexed with dephospho-IIAGlc.mBio. 2024 May 8;15(5):e0033024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00330-24. Epub 2024 Apr 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38564689 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription activation of two clusters for exopolysaccharide biosynthesis by phosphorylated DctD in Vibrio vulnificus.Environ Microbiol. 2021 Sep;23(9):5364-5377. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15636. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34110060
-
Negative regulation of sigma 54-dependent dctA expression by the transcriptional activator DctD.J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2674-81. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2674-2681.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8478332 Free PMC article.
-
Dicarboxylate transport by rhizobia.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004 Oct;28(4):489-501. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.04.002. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15374663 Review.
-
Exopolysaccharides from yeast: insight into optimal conditions for biosynthesis, chemical composition and functional properties - review.Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2015 Oct-Dec;14(4):283-292. doi: 10.17306/J.AFS.2015.4.29. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment. 2015. PMID: 28068035 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide analysis of quorum sensing regulon in marine fish pathogen Vibrio scophthalmi.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 12;14(1):27740. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78803-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39533010 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism for carbon catabolite repression of the chitin response in Vibrio cholerae.PLoS Genet. 2023 May 12;19(5):e1010767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010767. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37172034 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the transcriptionally active form of dephosphorylated DctD complexed with dephospho-IIAGlc.mBio. 2024 May 8;15(5):e0033024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00330-24. Epub 2024 Apr 2. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38564689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoch JA, Silhavy TJ (ed). 1995. Two-component signal transduction. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

