Target-Dependent Coordinated Biogenesis of Secondary MicroRNAs by miR-146a Balances Macrophage Activation Processes
- PMID: 35311564
- PMCID: PMC9022539
- DOI: 10.1128/mcb.00452-21
Target-Dependent Coordinated Biogenesis of Secondary MicroRNAs by miR-146a Balances Macrophage Activation Processes
Abstract
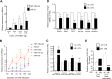
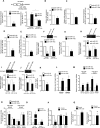
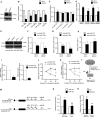
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) repress protein expression by binding to the target mRNAs. Exploring whether the expression of one miRNA can regulate the abundance and activity of other miRNAs, we noted the coordinated biogenesis of miRNAs in activated macrophages. miRNAs with higher numbers of binding sites (the "primary" miRNAs) induce expression of other miRNAs ("secondary" miRNAs) having binding sites on the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of common target mRNAs. miR-146a-5p, in activated macrophages, acts as a "primary" miRNA that coordinates biogenesis of "secondary" miR-125b, miR-21, or miR-142-3p to target new sets of mRNAs to balance the immune responses. During coordinated biogenesis, primary miRNA drives the biogenesis of secondary miRNA in a target mRNA- and Dicer1 activity-dependent manner. The coordinated biogenesis of miRNAs was observed across different cell types. The target-dependent coordinated miRNA biogenesis also ensures a cumulative mode of action of primary and secondary miRNAs on the secondary target mRNAs. Interestingly, using the "primary" miR-146a-5p-specific inhibitor, we could inhibit the target-dependent biogenesis of secondary miRNAs that can stop the miRNA-mediated buffering of cytokine expression and inflammatory response occurring in activated macrophages. Computational analysis suggests the prevalence of coordinated biogenesis of miRNAs also in other contexts in human and in mouse.
Keywords: activated macrophages; anti-inflammatory miRNAs; cooperative miRNA biogenesis; coordinated biogenesis of miRNAs; macrophage activation; macrophage polarization; miRNA biogenesis; primary miRNA; target mRNA-dependent miRNA biogenesis; target-dependent miRNA biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[The Interaction of miRNA-5p and miRNA-3p with the mRNAs of Orthologous Genes].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2019 Jul-Aug;53(4):692-704. doi: 10.1134/S0026898419040189. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2019. PMID: 31397443 Russian.
-
Time Series miRNA-mRNA integrated analysis reveals critical miRNAs and targets in macrophage polarization.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 16;6:37446. doi: 10.1038/srep37446. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27981970 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of Chicken miRNAs Associated with Monocyte to Macrophage Differentiation and Subsequent IFNγ Stimulated Activation.Microrna. 2017;6(1):53-70. doi: 10.2174/2211536605666161129122803. Microrna. 2017. PMID: 27897122
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-134-3p targets HMOX1 to inhibit ferroptosis in granulosa cells of sheep follicles.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Jan 2;17(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01328-6. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38166987 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes from MicroRNA-125b-Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote Wound Healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025;20(4):409-420. doi: 10.2174/011574888X287173240415050555. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 38659271
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
