The Identity of the Constriction Region of the Ribosomal Exit Tunnel Is Important to Maintain Gene Expression in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 35311583
- PMCID: PMC9045200
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02261-21
The Identity of the Constriction Region of the Ribosomal Exit Tunnel Is Important to Maintain Gene Expression in Escherichia coli
Abstract
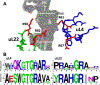
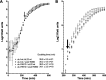
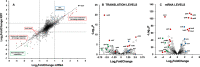
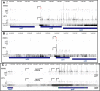
Mutational changes in bacterial ribosomes often affect gene expression and consequently cellular fitness. Understanding how mutant ribosomes disrupt global gene expression is critical to determining key genetic factors that affect bacterial survival. Here, we describe gene expression and phenotypic changes presented in Escherichia coli cells carrying an uL22(K90D) mutant ribosomal protein, which displayed alterations during growth. Ribosome profiling analyses revealed reduced expression of operons involved in catabolism, indole production, and lysine-dependent acid resistance. In general, translation initiation of proximal genes in several of these affected operons was substantially reduced. These reductions in expression were accompanied by increases in the expression of acid-induced membrane proteins and chaperones, the glutamate-decarboxylase regulon, and the autoinducer-2 metabolic regulon. In agreement with these changes, uL22(K90D) mutant cells had higher glutamate decarboxylase activity, survived better in extremely acidic conditions, and generated more biofilm in static cultures compared to their parental strain. Our work demonstrates that a single mutation in a non-conserved residue of a ribosomal protein affects a substantial number of genes to alter pH resistance and the formation of biofilms. IMPORTANCE All newly synthesized proteins must pass through a channel in the ribosome named the exit tunnel before emerging into the cytoplasm, membrane, and other compartments. The structural characteristics of the tunnel could govern protein folding and gene expression in a species-specific manner but how the identity of tunnel elements influences gene expression is less well-understood. Our global transcriptomics and translatome profiling demonstrate that a single substitution in a non-conserved amino acid of the E. coli tunnel protein uL22 has a profound impact on catabolism, cellular signaling, and acid resistance systems. Consequently, cells bearing the uL22 mutant ribosomes had an increased ability to survive acidic conditions and form biofilms. This work reveals a previously unrecognized link between tunnel identity and bacterial stress adaptation involving pH response and biofilm formation.
Keywords: acid resistance; biofilms; ribosomes; translational control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

