Fat mass and obesity associated (FTO)-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of Krüppel-like factor 3 (KLF3) promotes osteosarcoma progression
- PMID: 35311620
- PMCID: PMC9161850
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2051785
Fat mass and obesity associated (FTO)-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of Krüppel-like factor 3 (KLF3) promotes osteosarcoma progression
Abstract
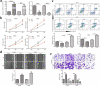
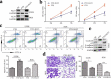
ARSTRACTN6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation is the most common and abundant methylation modification of eukaryotic mRNAs, which is involved in tumor initiation and progression. The study aims to explore the potential role and the regulatory mechanism of fat mass and obesity associated (FTO) in osteosarcoma (OS) progression. In this study, we detected the expressions of Krüppel-like factor 3 (KLF3) in OS cells and tissues and found that the mRNA and protein levels of KLF3 were increased in OS cells and tissues and significantly related to tumor size, metastasis, and TNM stage and poor prognosis of OS patients. FTO promoted the proliferation and invasion and suppressed apoptosis of OS cells through cell experiments in vitro. Further mechanism dissection revealed that FTO and YTHDF2 enforced the decay of KLF3 mRNA and decreased its expression. FTO-mediated mRNA demethylation inhibited KLF3 expression in the YTHDF2-dependent manner. Moreover, KLF3 overexpression abrogated FTO-induced oncogenic effects on the proliferation and invasion of OS cells. Overall, our findings showed that FTO-mediated m6A modification of KLF3 promoted OS progression, which may provide a therapeutic target for OS.
Keywords: FTO; KLF3; m6A methylation; osteosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes breast tumor progression through inhibiting BNIP3.Mol Cancer. 2019 Mar 28;18(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1004-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30922314 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor-suppressive effects of alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO via N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation on bladder cancer patients.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5323-5333. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1964893. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34499008 Free PMC article.
-
FTO demethylates m6A modifications in HOXB13 mRNA and promotes endometrial cancer metastasis by activating the WNT signalling pathway.RNA Biol. 2021 Sep;18(9):1265-1278. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1841458. Epub 2020 Nov 5. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33103587 Free PMC article.
-
Research advances of N6-methyladenosine in diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Sep;36(9):e24611. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24611. Epub 2022 Jul 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35837987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Roles of FTO in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 26;2022:2677312. doi: 10.1155/2022/2677312. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35528183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in osteosarcoma: expression, function and interaction with noncoding RNAs - an updated review.Epigenetics. 2023 Dec;18(1):2260213. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2260213. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37766615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of osteosarcoma metastasis and possible treatment opportunities.Front Oncol. 2023 May 1;13:1117867. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1117867. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37197432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF3 promotes colorectal cancer growth by activating WNT1.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):2475-2493. doi: 10.18632/aging.205494. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38305787 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances of m6A methylation in skeletal system disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 14;22(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-04944-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38355483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights into the Links between N6-Methyladenosine and Regulated Cell Death in Musculoskeletal Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Apr 24;14(5):514. doi: 10.3390/biom14050514. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785921 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G, et al. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1,702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(3):776–790. - PubMed
-
- Mialou V, Philip T, Kalifa C, et al. Metastatic osteosarcoma at diagnosis: prognostic factors and long-term outcome–the French pediatric experience. Cancer. 2005;104(5):1100–1109. - PubMed
-
- Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, et al. Current and future therapeutic approaches for osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018;18(1):39–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
