Arcuate NPY is involved in salt-induced hypertension via modulation of paraventricular vasopressin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- PMID: 35312067
- PMCID: PMC9544553
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30719
Arcuate NPY is involved in salt-induced hypertension via modulation of paraventricular vasopressin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Abstract
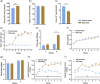
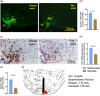
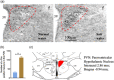
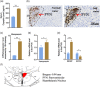
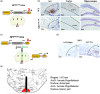
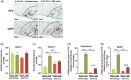
Chronic high salt intake is one of the leading causes of hypertension. Salt activates the release of the key neurotransmitters in the hypothalamus such as vasopressin to increase blood pressure, and neuropepetide Y (NPY) has been implicated in the modulation of vasopressin levels. NPY in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (Arc) is best known for its control in appetite and energy homeostasis, but it is unclear whether it is also involved in the development of salt-induced hypertension. Here, we demonstrate that wild-type mice given 2% NaCl salt water for 8 weeks developed hypertension which was associated with marked downregulation of NPY expression in the hypothalamic Arc as demonstrated in NPY-GFP reporter mice as well as by in situ hybridization analysis. Furthermore, salt intake activates neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) where mRNA expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and vasopressin was found to be upregulated, leading to elevated serum vasopressin levels. This finding suggests an inverse correlation between the Arc NPY level and expression of vasopressin and BDNF in the PVN. Specific restoration of NPY by injecting AAV-Cre recombinase into the Arc only of the NPY-targeted mutant mice carrying a loxP-flanked STOP cassette reversed effects of salt intake on vasopressin and BDNF expression, leading to a normalization of salt-dependent blood pressure. In summary, our study uncovers an important Arc NPY-originated neuronal circuitry that could sense and respond to peripheral electrolyte signals and thereby regulate hypertension via vasopressin and BDNF in the PVN.
Keywords: BDNF; hypertension; hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (Arc); neuropeptide Y (NPY); salt (NaCl); vasopressin.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular Physiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotine administration reduces neuropeptide Y and neuropeptide Y mRNA concentrations in the rat hypothalamus: NPY may mediate nicotine's effects on energy balance.Brain Res. 1995 Oct 2;694(1-2):139-46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00834-d. Brain Res. 1995. PMID: 8974638
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus reduces energy intake.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):R1003-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00011.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 20. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17581841
-
High salt intake enhances swim stress-induced PVN vasopressin cell activation and active stress coping.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Jul;93:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.003. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29684712 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide Y, the hypothalamus, and diabetes: insights into the central control of metabolism.Peptides. 1995;16(4):757-71. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)00200-p. Peptides. 1995. PMID: 7479313 Review.
-
The hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis: lifting the lid on a black box.Proc Nutr Soc. 2000 Aug;59(3):385-96. doi: 10.1017/s0029665100000434. Proc Nutr Soc. 2000. PMID: 10997654 Review.
Cited by
-
The combined effect of metformin and mirabegron on diet-induced obesity.MedComm (2020). 2023 Feb 14;4(2):e207. doi: 10.1002/mco2.207. eCollection 2023 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 36818016 Free PMC article.
-
Central nervous system mechanisms of salt-sensitive hypertension.Physiol Rev. 2025 Oct 1;105(4):1989-2032. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2024. Epub 2025 May 2. Physiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40315132 Review.
-
Gender-specific Single Transcript Level Atlas of Vasopressin and its Receptor (AVPR1a) in the Mouse Brain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 10:2024.12.09.627541. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.09.627541. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39713333 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The interaction of BDNF with estrogen in the development of hypertension and obesity, particularly during menopause.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Nov 25;15:1384159. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1384159. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39655343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiency of neuropeptide Y attenuates neointima formation after vascular injury in mice.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 May 6;23(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03267-y. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37149580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choe, K. Y. , Han, S. Y. , Gaub, P. , Shell, B. , Voisin, D. L. , Knapp, B. A. , & Bourque, C. W. (2015). High salt intake increases blood pressure via BDNF‐mediated downregulation of KCC2 and impaired baroreflex inhibition of vasopressin neurons. Neuron, 85(3), 549–560. 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.048 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

