Transcriptomic profiling of blood from autoimmune hepatitis patients reveals potential mechanisms with implications for management
- PMID: 35312680
- PMCID: PMC8936448
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264307
Transcriptomic profiling of blood from autoimmune hepatitis patients reveals potential mechanisms with implications for management
Abstract
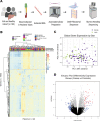
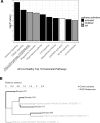
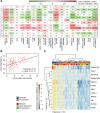
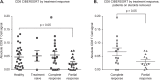
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a poorly understood, chronic disease, for which corticosteroids are still the mainstay of therapy and most patients undergo liver biopsy to obtain a diagnosis. We aimed to determine if there was a transcriptomic signature of AIH in the peripheral blood and investigate underlying biologic pathways revealed by gene expression analysis. Whole blood RNA from 75 AIH patients and 25 healthy volunteers was extracted and sequenced. Differential gene expression analysis revealed 249 genes that were significantly differentially expressed in AIH patients compared to controls. Using a random forest algorithm, we determined that less than 10 genes were sufficient to differentiate the two groups in our cohort. Interferon signaling was more active in AIH samples compared to controls, regardless of treatment status. Pegivirus sequences were detected in five AIH samples and 1 healthy sample. The gene expression data and clinical metadata were used to determine 12 genes that were significantly associated with advanced fibrosis in AIH. AIH patients with a partial response to therapy demonstrated decreased evidence of a CD8+ T cell gene expression signal. These findings represent progress in understanding a disease in need of better tests, therapies, and biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines From the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases—Mack—- Hepatology—Wiley Online Library [Internet]. [cited 2020 Jun 8]. Available from: https://aasldpubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.31065 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Comerford M, Fogel R, Bailey JR, Chilukuri P, Chalasani N, Lammert CS. Leveraging Social Networking Sites for an Autoimmune Hepatitis Genetic Repository: Pilot Study to Evaluate Feasibility. J Med Internet Res [Internet]. 2018. Jan 18 [cited 2019 Feb 28];20(1). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5795096/ doi: 10.2196/jmir.7683 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

