Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx@ZnO Hollow Spheres with Excellent Microwave Absorption Inspired by the Visual Phenomenon of Eyeless Urchins
- PMID: 35312846
- PMCID: PMC8938554
- DOI: 10.1007/s40820-022-00817-5
Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx@ZnO Hollow Spheres with Excellent Microwave Absorption Inspired by the Visual Phenomenon of Eyeless Urchins
Abstract
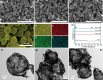
Ingenious microstructure design and rational composition selection are effective approaches to realize high-performance microwave absorbers, and the advancement of biomimetic manufacturing provides a new strategy. In nature, urchins are the animals without eyes but can "see", because their special structure composed of regular spines and spherical photosensitive bodies "amplifies" the light-receiving ability. Herein, inspired by the above phenomenon, the biomimetic urchin-like Ti3C2Tx@ZnO hollow microspheres are rationally designed and fabricated, in which ZnO nanoarrays (length: ~ 2.3 μm, diameter: ~ 100 nm) as the urchin spines are evenly grafted onto the surface of the Ti3C2Tx hollow spheres (diameter: ~ 4.2 μm) as the urchin spherical photosensitive bodies. The construction of gradient impedance and hierarchical heterostructures enhance the attenuation of incident electromagnetic waves. And the EMW loss behavior is further revealed by limited integral simulation calculations, which fully highlights the advantages of the urchin-like architecture. As a result, the Ti3C2Tx@ZnO hollow spheres deliver a strong reflection loss of - 57.4 dB and broad effective absorption bandwidth of 6.56 GHz, superior to similar absorbents. This work provides a new biomimetic strategy for the design and manufacturing of advanced microwave absorbers.
Keywords: Bioinspired; Hierarchical heterostructures; Microwave absorption; Ti3C2Tx MXene; ZnO nanoarrays.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gradient Hierarchical Hollow Heterostructures of Ti3C2Tx@rGO@MoS2 for Efficient Microwave Absorption.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Jul 12;15(27):32803-32813. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c06860. Epub 2023 Jun 27. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 37366118
-
3D Ultralight Hollow NiCo Compound@MXene Composites for Tunable and High-Efficient Microwave Absorption.Nanomicro Lett. 2021 Oct 11;13(1):206. doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00727-y. Nanomicro Lett. 2021. PMID: 34633551 Free PMC article.
-
Graphene-Wrapped Magnetic Multichamber Ti3C2Tx Spheres for Stable Broadband Microwave Absorption.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Sep 25;16(38):51118-51128. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c10905. Epub 2024 Sep 13. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39271249
-
Bamboo-Inspired Hierarchically Hollow Aerogel MXene Fibers with Ultrafast Ionic Channels and Multiple Electromagnetic Wave Attenuation Routes Toward High-Performance Supercapacitors and Microwave Absorption.Small. 2025 Mar;21(10):e2412272. doi: 10.1002/smll.202412272. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Small. 2025. PMID: 39806824
-
Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ni Chain/ZnO Array Hybrid Nanostructures on Cotton Fabric for Durable Self-Cleaning and Enhanced Microwave Absorption.ACS Nano. 2020 Jul 28;14(7):8634-8645. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03013. Epub 2020 Jul 9. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32628459
Cited by
-
Ni-Carbon Microtube/Polytetrafluoroethylene as Flexible Electrothermal Microwave Absorbers.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Nov;10(31):e2304218. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304218. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37721442 Free PMC article.
-
Flexible Polydimethylsiloxane Composite with Multi-Scale Conductive Network for Ultra-Strong Electromagnetic Interference Protection.Nanomicro Lett. 2022 Dec 29;15(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00990-7. Nanomicro Lett. 2022. PMID: 36580201 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of MXene/BN Composites with Adjustable Microwave Absorption Performance.Materials (Basel). 2023 Oct 18;16(20):6752. doi: 10.3390/ma16206752. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895733 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from Nature: Advances and Perspectives in Bionic Microwave Absorption Materials.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Dec 30;17(1):100. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01591-2. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 39739207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D Printing of Periodic Porous Metamaterials for Tunable Electromagnetic Shielding Across Broad Frequencies.Nanomicro Lett. 2024 Sep 3;16(1):279. doi: 10.1007/s40820-024-01502-5. Nanomicro Lett. 2024. PMID: 39225896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song P, Liu B, Liang C, Ruan K, Qiu H, et al. Lightweight, flexible cellulose-derived carbon aerogel@reduced graphene oxide/PDMS composites with outstanding EMI shielding performances and excellent thermal conductivities. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021;13:91. doi: 10.1007/s40820-021-00624-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
