The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in China: Results from the Cross-Sectional CAPTURE Study
- PMID: 35312971
- PMCID: PMC9076769
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-022-01243-x
The Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in China: Results from the Cross-Sectional CAPTURE Study
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes (T2D), and treatment guidelines have increasingly focused on the comprehensive management of T2D and CVD. Here, we report data from the Chinese population within the CAPTURE study, including CVD prevalence in patients with T2D and insights into their management.
Methods: CAPTURE (a multinational, non-interventional, cross-sectional study in adults with T2D) included data from eight centers in China from July to September 2019. Overall CVD prevalence estimates were calculated, and descriptive data regarding CVD subtypes and treatment were collected and reported here.
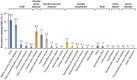
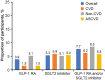
Results: Of 805 adults with T2D enrolled in China (61.9% male, median age 59 years), 273 had established CVD, with an estimated prevalence (95% CI) of 33.9% (30.6%, 37.3%). Most CVD cases were atherosclerotic (94.9%). Coronary heart disease had the highest estimated prevalence (16.0%), followed by carotid artery disease (9.6%) and cerebrovascular disease (7.7%). Use of glucose-lowering agents (GLAs) with proven cardiovascular benefits (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and/or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors) was low in the China sample (7.7%). Approximately half of the CVD subgroup in the China sample was receiving cardiovascular medication, but use of guideline-directed agents was low (e.g., statins: 35.9%; angiotensin II receptor blockers: 15%; angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: 2.6%).
Conclusions: In the Chinese CAPTURE population, one-third of patients had established CVD, with atherosclerotic CVD largely accounting for the CVD burden; use of GLAs with proven cardiovascular benefits and cardiovascular medications was low, suggesting an unmet need for optimal management in this group.
Keywords: Cardiovascular diseases; China; Cross-sectional studies; Prevalence; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

