The synthetic triterpenoids CDDO-TFEA and CDDO-Me, but not CDDO, promote nuclear exclusion of BACH1 impairing its activity
- PMID: 35313207
- PMCID: PMC8938334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102291
The synthetic triterpenoids CDDO-TFEA and CDDO-Me, but not CDDO, promote nuclear exclusion of BACH1 impairing its activity
Abstract
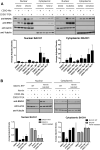
The transcription factor BACH1 is a potential therapeutic target for a variety of chronic conditions linked to oxidative stress and inflammation, as well as cancer metastasis. However, only a few BACH1 degraders/inhibitors have been described. BACH1 is a transcriptional repressor of heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), which is positively regulated by transcription factor NRF2 and is highly inducible by derivatives of the synthetic oleanane triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO). Most of the therapeutic activities of these compounds are due to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which are widely attributed to their ability to activate NRF2. However, with such a broad range of action, these compounds have other molecular targets that have not been fully identified and could also be of importance for their therapeutic profile. Herein we identified BACH1 as a target of two CDDO-derivatives (CDDO-Me and CDDO-TFEA), but not of CDDO. While both CDDO and CDDO-derivatives activate NRF2 similarly, only CDDO-Me and CDDO-TFEA inhibit BACH1, which explains the much higher potency of these CDDO-derivatives as HMOX1 inducers compared with unmodified CDDO. Notably, we demonstrate that CDDO-Me and CDDO-TFEA inhibit BACH1 via a novel mechanism that reduces BACH1 nuclear levels while accumulating its cytoplasmic form. In an in vitro model, both CDDO-derivatives impaired lung cancer cell invasion in a BACH1-dependent and NRF2-independent manner, while CDDO was inactive. Altogether, our study identifies CDDO-Me and CDDO-TFEA as dual KEAP1/BACH1 inhibitors, providing a rationale for further therapeutic uses of these drugs.
Keywords: BACH1; CDDO; HMOX1; NRF2.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: ADK is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Evgen Pharma, and a consultant for Aclipse Therapeutics.
Figures




References
-
- Wang Y., Porter W.W., Suh N., Honda T., Gribble G.W., Leesnitzer L.M., et al. A synthetic triterpenoid, 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO), is a ligand for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000;14(10):1550–1556. - PubMed
-
- Konopleva M., Tsao T., Ruvolo P., Stiouf I., Estrov Z., Leysath C.E., et al. Novel triterpenoid CDDO-Me is a potent inducer of apoptosis and differentiation in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 2002;99(1):326–335. - PubMed
-
- Liby K., Royce D.B., Williams C.R., Risingsong R., Yore M.M., Honda T., et al. The synthetic triterpenoids CDDO-methyl ester and CDDO-ethyl amide prevent lung cancer induced by vinyl carbamate in A/J mice. Cancer Res. 2007;67(6):2414–2419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

