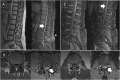
Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy after the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine may follow a chronic course
- PMID: 35313224
- PMCID: PMC8923716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2022.120231
Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy after the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine may follow a chronic course
Abstract
Background: Rare autoimmune neurological events have been reported during the ongoing global drive for mass vaccination as a means of controlling the Covid-19 pandemic. Guillain-Barré syndrome, an acute inflammatory neuropathy well recognised as a rare complication of influenza vaccination, has been reported to follow administration of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca) vaccine.
Methods: We report four patients with inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy after vaccination in whom a relapsing or progressive course indicated the development of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP).
Conclusions: Awareness of this complication and distinction from Guillain-Barré syndrome enables the timely institution of maintenance immunomodulatory treatment. Our report also highlights the likely relationship between vaccination and the subsequent development of CIDP, but definitive demonstration of a causal link needs larger studies.
Keywords: AstraZeneca vaccine; CIDP; Covid-19; Guillain-Barré syndrome; Inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Schonberger L.B., Bregman D.J., Sullivan-Bolyai J.Z., et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome following vaccination in the National Influenza Immunization Program, United States, 1976–1977. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1979;110(2):105–123. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical