Evaluation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Mortality Risk in Preterm Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis
- PMID: 35313308
- PMCID: PMC9117503
- DOI: 10.1159/000522560
Evaluation of the Neonatal Sequential Organ Failure Assessment and Mortality Risk in Preterm Infants with Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Abstract
Introduction: The neonatal sequential organ failure assessment (nSOFA) score is a tool for calculating mortality risk of infants in the neonatal intensive care unit. The utility of the nSOFA in determining the risk of mortality or the association with surgical intervention among infants with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) has not been investigated.
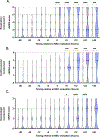
Methods: We performed a retrospective, cohort study of preterm (<37 weeks) infants with NEC Bell's stage ≥ IIA at six hospitals from 2008 to 2020. An nSOFA score (range 0-15) was assigned to each patient at nine time points from 48 h before or after clinical illness was suspected.
Results: Of the 259 infants, nSOFA scores for infants who died (n = 39) or had the composite outcome of surgery or death (n = 114) were significantly higher (p < 0.05) early in the NEC course compared to nSOFA scores for infants who survived medical NEC. Twelve hours after evaluation, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.87 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.80-0.93) to discriminate for mortality and 0.84 (95% CI, 0.79-0.90) for surgery or death (p < 0.001). A maximum nSOFA score of ≥4 at -6, 0, 6, or 12 h following evaluation was associated with a 20-fold increase in mortality and 19-fold increase in surgery or death compared with a score of <4 (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In this multicenter cohort, the nSOFA score was able to discriminate well for death as well as surgery or death among infants with NEC. The nSOFA is a clinical research tool that may be used in infants with NEC to improve classification by objective quantification of organ dysfunction.
Keywords: Illness severity; Necrotizing enterocolitis; Neonate; Organ dysfunction.
© 2022 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures




References
-
- Henry MC, Moss RL. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2008. May;17(2):98–109. - PubMed

