Normative data for ulnar nerve conduction and the influence of gender and height on ulnar nerve conduction velocity in healthy Nigerians
- PMID: 35313404
- PMCID: PMC9020630
- DOI: 10.4103/aam.aam_74_20
Normative data for ulnar nerve conduction and the influence of gender and height on ulnar nerve conduction velocity in healthy Nigerians
Abstract
Background: Despite the usefulness of ulnar nerve conduction studies in identifying disorders of ulnar nerves, there is a lack of normative values for the ulnar nerve in Nigerian population.
Objective: The objective of the study was to generate normative values for motor and sensory ulnar nerve conduction studies (NCSs) in Nigerian population and to determine the influence of gender and height on ulnar nerve conduction velocity (NCV).
Materials and methods: A total of 200 healthy volunteers were selected after clinical evaluation to exclude common causes of ulnar neuropathy. We carried out NCS of ulnar nerves on all the healthy volunteers according to a standardized protocol. The NCS parameters included in the final analysis were amplitude, latency, NCV, and f-wave latency. Ethical approval was obtained for the study.
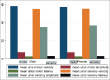
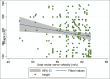
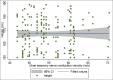
Results: The mean ulnar nerve sensory velocity was 55.22 ± 5.67 with 2.5 and 97.5 percentile of 46.9 and 70.1, respectively. The mean latency of the ulnar nerve (sensory) was 2.97 ± 0.62 with 2.5 and 97.5 percentile of 2.00 and 4.52, respectively. The mean amplitude of the ulnar nerve (sensory) was 35.56 ± 9.97 with 2.5 and 97.5 percentile of 15.9 and 57.7, respectively). The ulnar NCV was significantly (P = 0.0202) higher in male. Mild inverse correlation (r = 0.2) was found between ulnar NCV and height of the participants (P = 0.0089).
Conclusion: In the Nigerian population, normative values of motor and sensory ulnar nerve conduction parameters are similar to the existing values in the literature. The ulnar NCV appeared to be influenced by height and gender.
Résumé Contexte: Malgré l'utilité des études de conduction du nerf ulnaire pour identifier les troubles des nerfs ulnaire, il y a un manque de normative valeurs pour le nerf ulnaire dans la population nigériane. Objectif: L'objectif de l'étude était de générer des valeurs normatives pour les moteurs et études de conduction sensorielle du nerf ulnaire (NCS) dans la population nigériane et pour déterminer l'influence du sexe et de la taille sur le nerf ulnaire vitesse de conduction (NCV). Matériel et méthodes: Un total de 200 volontaires sains ont été sélectionnés après évaluation clinique pour exclure causes courantes de neuropathie ulnaire. Nous avons réalisé une NCS des nerfs ulnaire sur tous les volontaires sains selon un protocole standardisé.Les paramètres NCS inclus dans l'analyse finale étaient l'amplitude, la latence, la NCV et la latence de l'onde f. L'approbation éthique a été obtenue pour le étude. Résultats: La vitesse sensorielle moyenne du nerf ulnaire était de 55,22 ± 5,67 avec 2,5 et 97,5 percentile de 46,9 et 70,1, respectivement. La moyenne la latence du nerf ulnaire (sensoriel) était de 2,97 ± 0,62 avec 2,5 et 97,5 percentile de 2,00 et 4,52, respectivement. L'amplitude moyenne de l'ulnaire nerf (sensoriel) était de 35,56 ± 9,97 avec 2,5 et 97,5 percentile de 15,9 et 57,7, respectivement). Le NCV ulnaire était significativement (P = 0,0202)plus élevé chez les hommes. Une légère corrélation inverse (r = 0,2) a été trouvée entre la NCV ulnaire et la taille des participants (P = 0,0089). Conclusion: dans la population nigériane, les valeurs normatives des paramètres de conduction du nerf ulnaire moteur et sensoriel sont similaires aux valeurs existantes dans le Littérature. Le NCV ulnaire semble être influencé par la taille et le sexe. Mots-clés: Électromyographie, test de conduction nerveuse, Nigérians, normatif, nerf cubital.
Keywords: Electromyography; Nigerians; nerve conduction test; normative; ulnar nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Median Nerve Conduction in Healthy Nigerians: Normative Data.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2016 Mar-Apr;6(2):85-9. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.181839. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2016. PMID: 27213090 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between skin temperature and neuronal characteristics in the median, ulnar and radial nerves of non-impaired individuals.Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 Nov-Dec;47(7-8):351-60. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 18051629
-
Effects of gender and age on median and ulnar nerve sensory responses over ring finger.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2014 Feb;24(1):52-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2014. PMID: 24387997
-
[Inter-examiner reliability of nerve conduction measurements].No To Shinkei. 1999 Dec;51(12):1029-32. No To Shinkei. 1999. PMID: 10654297 Japanese.
-
Diagnostic utility of ultrasonography versus nerve conduction studies in mild carpal tunnel syndrome.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Mar 15;59(3):357-66. doi: 10.1002/art.23317. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18311762 Review.
Cited by
-
Nerve Conduction Differences in a Large Clinical Population: The Role of Age and Sex.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2023;10(5):925-935. doi: 10.3233/JND-230052. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2023. PMID: 37545257 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Specific Differences in Peripheral Nerve Properties: A Comparative Analysis of Conduction Velocity and Cross-Sectional Area in Upper and Lower Limbs.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;14(23):2711. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232711. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benatar M, Wuu J, Peng L. Reference data for commonly used sensory and motor nerve conduction studies. Muscle Nerve. 2009;40:772–94. - PubMed
-
- Hennessey WJ, Falco FJ, Braddom RL. Median and ulnar nerve conduction studies: Normative data for young adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994;75:259–64. - PubMed
-
- Falco FJ, Hennessey WJ, Braddom RL, Goldberg G. Standardized nerve conduction studies in the upper limb of the healthy elderly. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1992;71:263–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

