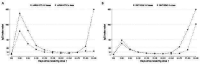This is a preprint.
SARS-CoV-2 infection during the Omicron surge among patients receiving dialysis: the role of circulating receptor-binding domain antibodies and vaccine doses
- PMID: 35313586
- PMCID: PMC8936102
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.03.15.22272426
SARS-CoV-2 infection during the Omicron surge among patients receiving dialysis: the role of circulating receptor-binding domain antibodies and vaccine doses
Update in
-
SARS-CoV-2 Infection during the Omicron Surge among Patients Receiving Dialysis: The Role of Circulating Receptor-Binding Domain Antibodies and Vaccine Doses.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Oct;33(10):1832-1839. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022040504. Epub 2022 Aug 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35973733 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: It is unclear whether a third dose of mRNA platform vaccines, or antibody response to prior infection or vaccination confer protection from the Omicron variant among patients receiving dialysis.
Methods: Monthly since February 2021, we tested plasma from 4,697 patients receiving dialysis for antibodies to the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2. We assessed semiquantitative median IgG index values over time among patients vaccinated with at least one dose of the two mRNA vaccines. We ascertained documented COVID-19 diagnoses after December 25, 2021 and up to January 31, 2022. We estimated the relative risk for documented SARS-CoV-2 infection by vaccination status using a log-binomial model accounting for age, sex, and prior clinical COVID-19. Among patients with RBD IgG index value available during December 1-December 24, 2021, we also evaluated the association between the circulating RBD IgG titer and risk for Omicron variant SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Results: Of the 4,697 patients we followed with monthly RBD assays, 3576 are included in the main analysis cohort; among these, 852 (24%) were unvaccinated. Antibody response to third doses was robust (median peak index IgG value at assay limit of 150, equivalent to 3270 binding antibody units/mL). Between December 25-January 31, 2022, SARS-CoV-2 infection was documented 340 patients (7%), 115 (36%) of whom were hospitalized. The final doses of vaccines were given a median of 272 (25 th , 75 th percentile, 245-303) days and 58 (25 th , 75 th percentile, 51-95) days prior to infection for the 1-2 dose and 3 dose vaccine groups respectively. Relative risks for infection were higher among patients without vaccination (RR 2.1 [95%CI 1.6, 2.8]), and patients with 1-2 doses (RR 1.3 [95%CI 1.0, 1.8]), compared with patients with three doses of the mRNA vaccines. Relative risks for infection were higher among patients with RBD index values < 23 (506 BAU/mL), compared with RBD index value ≥ 23 (RR 2.4 [95%CI 1.9, 3.0]). The higher risk for infection among patients with RBD index values < 23 was present among patients who received three doses (RR 2.1 [95%CI 1.3, 3.4]).
Conclusions: Among patients receiving hemodialysis, patients unvaccinated, without a third mRNA vaccine dose, or those lacking robust circulating antibody response are at higher risk for Omicron variant infection. Low circulating antibodies could identify the subgroup needing intensified surveillance, prophylaxis or treatment in this patient population.
Figures
References
-
- Hasmann S, Paal M, Fuessl L, Fischereder M, Schonermarck U. Humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in haemodialysis patients: (Response to: Humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in renal transplant versus dialysis patients: A prospective, multicenter observational study using mRNA-1273 or BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.). Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2021;10:100237. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous