Correlation of LAGE3 with unfavorable prognosis and promoting tumor development in HCC via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/RAF/MAPK pathways
- PMID: 35313850
- PMCID: PMC8939149
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09398-3
Correlation of LAGE3 with unfavorable prognosis and promoting tumor development in HCC via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/RAF/MAPK pathways
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common clinical malignancies quite susceptible to recurrence and metastasis. Despite several improvements in therapeutic approaches, the prognosis remains poor due to the limited treatment options. A bioinformatics analysis based on TCGA databases revealed that the recombinant human L antigen family member 3 (LAGE3) might function as an effective prognostic and diagnostic biomarker for HCC, as LAGE3, a protein-coding gene, maintains several important biological functions and has a physiological significance in the CTAG family while simultaneously being involved in regulating the occurrence and invasion of numerous types of tumors. However, the LAGE3 gene's functional and regulatory mechanism in the progression of HCC remains unclear.
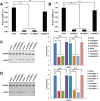
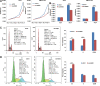
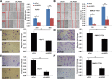
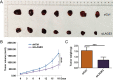
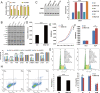
Methods: The LAGE3 level was investigated in 79 HCC tissues cases, ten HCC adjacent tissue cases, and six cases of normal liver tissues by IHC, while the LAGE3 level was evaluated in BEL-7404, SMCC-7721, Huh-7, HepG2, and MIHA cell lines by qRT-PCR and Western blot tests. Although the proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptotic abilities of HCC cells were measured in vitro after silencing assay to probe the role of LAGE3 in HCC cells, the tumor xenograft growth experiment was used to verify the in vivo effect of LAGE3 gene knockdown on the growth of HCC tumors combined with bioinformatics analysis to study the LAGE3 mechanisms regulating HCC proliferation.
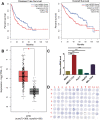
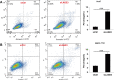
Results: Our results implied that LAGE3 was extensively expressed in HCC cell lines like BEL-7404, SMCC-7721, and Huh-7 cells as well as HCC tissues, but a lower expression was observed in HepG2 cells. Additionally, LAGE3 restrains cellular proliferation, promotes apoptotic pathways in HCC cells, and inhibits the growth of HCC tumors in vivo. Lastly, it was stated that LAGE3 might promote tumor development in HCC via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/RAF/MAPK pathways.
Conclusion: This study shows that the development of specific LAGE3 target drugs might become new effective treatment modalities for HCC patients.
Keywords: Apoptosis; HCC; Invasion; LAGE3; Migration; Proliferation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LAGE3 promoted cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and inhibited cell apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by facilitating the JNK and ERK signaling pathway.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021 Nov 27;26(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00295-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34837962 Free PMC article.
-
PI-103 and sorafenib inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways.Anticancer Res. 2010 Dec;30(12):4951-8. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21187475 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical efficacy of a novel dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, CMG002, alone and in combination with sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;84(4):809-817. doi: 10.1007/s00280-019-03918-y. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31385002
-
Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2020 May;235(5):4146-4152. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29333. Epub 2019 Oct 29. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31663122 Review.
-
The Role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;24(3):2652. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032652. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals the metabolic changes and the prognostic value of malignant hepatocyte subpopulations and predict new therapeutic agents for hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 31;13:1104262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1104262. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36860314 Free PMC article.
-
Isosteviol plays a protective role on hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice through MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 23;9:66. doi: 10.21037/tgh-23-66. eCollection 2024. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39503028 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs in immune infiltration and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05091-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36597032 Free PMC article.
-
EWS/FLI1 Characterization, Activation, Repression, Target Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Ewing Sarcoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 14;24(20):15173. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACYP2 functions as an innovative nano-therapeutic target to impede the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the activity of TERT and the KCNN4/ERK pathway.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Sep 12;22(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02827-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39267048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rashed WM, Kandeil MAM, Mahmoud MO, Ezzat S. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Egypt: a comprehensive overview. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2020;32:5. - PubMed
-
- Feld JJ, Krassenburg LAP. What comes first: treatment of viral hepatitis or liver Cancer? Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1041–1049. - PubMed
-
- Dong X, Lv S, Zhang X, Hao R. Upregulation of LAGE3 correlates with prognosis and immune infiltrates in colorectal cancer: a bioinformatic analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106599. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

