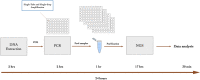
A comprehensive HPV-STI NGS assay for detection of 29 HPV types and 14 non-HPV sexually transmitted infections
- PMID: 35313939
- PMCID: PMC8935747
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-022-00420-8
A comprehensive HPV-STI NGS assay for detection of 29 HPV types and 14 non-HPV sexually transmitted infections
Abstract
Background: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are prevalent throughout the world and impose a significant burden on individual health and public health systems. Missed diagnosis and late treatment of STIs can lead to serious complications such as infertility and cervical cancer. Although sexually transmitted co-infections are common, most commercial assays target one or a few STIs. The HPV-STI ChapterDx Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) assay detects and quantifies 29 HPVs and 14 other STIs in a single-tube and single-step PCR reaction and can be applied to tens to thousands of samples in a single sequencing run.
Methods: A cohort of 274 samples, previously analyzed by conventional cytology/histology and Roche cobas HPV Test, were analyzed by ChapterDx HPV-STI NGS assay for detection of 43 HPV and STI. A set of 43 synthetic control DNA fragments for 43 HPV and STI were developed to evaluate the limit of detection, specificity, and sensitivity of ChapterDx HPV-STI NGS assay.
Results: The assay was evaluated in this study, and the limit of detection was 100% at 50 copies for all targets, and 100%, 96%, 88% at 20 copies for 34, 8, and 1 target, respectively. The performance of this assay has been compared to Roche cobas HPV test, showing an overall agreement of 97.5% for hr-HPV, and 98.5% for both, HPV16 and HPV18. The assay also detected all HPV-infected CIN2/3 with 100% agreement with Roche cobas HPV results. Moreover, several co-infections with non-HPV STIs, such as C. trachomatis, T. vaginalis, M. genitalium, and HSV2 were identified.
Conclusions: The ChapterDx HPV-STI NGS assay is a user-friendly, easy to automate and cost-efficient assay, which provides accurate and comprehensive results for a wide spectrum of HPVs and STIs.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Chlamydia trachomatis; HPV genotyping; Human papillomavirus (HPV); Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Next generation sequencing (NGS); Sexually transmitted disease (STD); Sexually transmitted infections (STI); Treponema pallidum; Trichomonas vaginalis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ZM, BG, and CW are shareholders and employees of Chapter Diagnostics. A patent has been issued for the technology. The INEI-ANLIS Malbrán investigators declare no competing interests; they did not receive any financial contribution from Chapter Diagnostics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A New Multiplex Genetic Detection Assay Method for the Rapid Semi-Quantitative Detection of Six Common Curable Sexually Transmitted Pathogens From the Genital Tract.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Aug 23;11:704037. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.704037. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34497776 Free PMC article.
-
High molecular prevalence of HPV and other sexually transmitted infections in a population of asymptomatic women who work or study at a Brazilian university.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021 Jan 20;63:e1. doi: 10.1590/S1678-9946202163001. eCollection 2021. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021. PMID: 33503149 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections and human papillomavirus in cervical samples from incarcerated women in São Paulo, Brazil: a retrospective single-center study.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 23;12:1353845. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1353845. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39109153 Free PMC article.
-
The vaginal microbiota and its association with human papillomavirus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Mycoplasma genitalium infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Jan;25(1):35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.04.019. Epub 2018 May 3. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 29729331 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections (STI) using self-collected non-invasive specimens.Sex Health. 2004;1(2):121-6. doi: 10.1071/sh03014. Sex Health. 2004. PMID: 16334994 Review.
Cited by
-
Virome capture sequencing for comprehensive HPV genotyping in cervical samples.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251334515. doi: 10.1177/00368504251334515. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40232222 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a targeted amplicon sequencing method for genotyping Cyclospora cayetanensis from fresh produce and clinical samples with enhanced genomic resolution and sensitivity.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 16;14:1212863. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1212863. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37396378 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual Blood as a Diagnostic Specimen for Human Papillomavirus Genotyping and Genital Tract Infection Using Next-Generation Sequencing as a Novel Diagnostic Tool.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 25;14(7):686. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14070686. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611599 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the interrelated nature of vaginal microecology, HPV infection, and cervical lesions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 19;15:1608195. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1608195. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40612393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Munoz N, Bosch FX, de Sanjose S, Herrero R, Castellsague X, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ. International Agency for Research on Cancer Multicenter Cervical Cancer Study G: epidemiologic classification of human papillomavirus types associated with cervical cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(6):518–527. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa021641. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials