Development of off-the-shelf hematopoietic stem cell-engineered invariant natural killer T cells for COVID-19 therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 35313965
- PMCID: PMC8935266
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02787-2
Development of off-the-shelf hematopoietic stem cell-engineered invariant natural killer T cells for COVID-19 therapeutic intervention
Abstract
Background: New COVID-19 treatments are desperately needed as case numbers continue to rise and emergent strains threaten vaccine efficacy. Cell therapy has revolutionized cancer treatment and holds much promise in combatting infectious disease, including COVID-19. Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells are a rare subset of T cells with potent antiviral and immunoregulatory functions and an excellent safety profile. Current iNKT cell strategies are hindered by the extremely low presence of iNKT cells, and we have developed a platform to overcome this critical limitation.
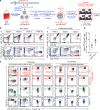
Methods: We produced allogeneic HSC-engineered iNKT (AlloHSC-iNKT) cells through TCR engineering of human cord blood CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and differentiation of these HSCs into iNKT cells in an Ex Vivo HSC-Derived iNKT Cell Culture. We then established in vitro SARS-CoV-2 infection assays to assess AlloHSC-iNKT cell antiviral and anti-hyperinflammation functions. Lastly, using in vitro and in vivo preclinical models, we evaluated AlloHSC-iNKT cell safety and immunogenicity for off-the-shelf application.
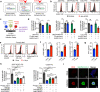
Results: We reliably generated AlloHSC-iNKT cells at high-yield and of high-purity; these resulting cells closely resembled endogenous human iNKT cells in phenotypes and functionalities. In cell culture, AlloHSC-iNKT cells directly killed SARS-CoV-2 infected cells and also selectively eliminated SARS-CoV-2 infection-stimulated inflammatory monocytes. In an in vitro mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) assay and an NSG mouse xenograft model, AlloHSC-iNKT cells were resistant to T cell-mediated alloreaction and did not cause GvHD.
Conclusions: Here, we report a method to robustly produce therapeutic levels of AlloHSC-iNKT cells. Preclinical studies showed that these AlloHSC-iNKT cells closely resembled endogenous human iNKT cells, could reduce SARS-CoV-2 virus infection load and mitigate virus infection-induced hyperinflammation, and meanwhile were free of GvHD-risk and resistant to T cell-mediated allorejection. These results support the development of AlloHSC-iNKT cells as a promising off-the-shelf cell product for treating COVID-19; such a cell product has the potential to target the new emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants as well as the future new emerging viruses.
Keywords: Allogeneic adoptive cell transfer; Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19); Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC); Invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cell; Off-the-shelf cellular product; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y.-R. L. and L.Y. are inventors on patent relating to this study filed by the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA); the patent has been licensed by Appia Bio. J.Y. is currently an employee of Appia Bio. P.W. and L.Y. are cofounders of Appia Bio, and have consulting, equity, and board relationships with Appia Bio. All other authors declare no competing interests. The declared company did not contribute to or direct any of the research reported in this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Off-the-shelf third-party HSC-engineered iNKT cells for ameliorating GvHD while preserving GvL effect in the treatment of blood cancers.iScience. 2022 Aug 6;25(9):104859. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104859. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36034226 Free PMC article.
-
Development of allogeneic HSC-engineered iNKT cells for off-the-shelf cancer immunotherapy.Cell Rep Med. 2021 Nov 16;2(11):100449. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100449. eCollection 2021 Nov 16. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 34841295 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Hematopoietic Stem Cell-Engineered Invariant Natural Killer T Cell Therapy for Cancer.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Oct 3;25(4):542-557.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 31495780 Free PMC article.
-
Invariant Natural Killer T Cells As Suppressors of Graft-versus-Host Disease in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 31;8:900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00900. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28824628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traversing the bench to bedside journey for iNKT cell therapies.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1436968. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436968. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39170618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deficiency and dysfunctional roles of natural killer T cells in patients with ARDS.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 30;15:1433028. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1433028. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39281681 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol to profile tumor and microenvironment from ovarian cancer patient samples and evaluate cell-based therapy using in vitro killing assays.STAR Protoc. 2025 Jun 20;6(2):103742. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103742. Epub 2025 Apr 5. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40188433 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal-associated invariant T cells for cancer immunotherapy.Mol Ther. 2023 Mar 1;31(3):631-646. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.11.019. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36463401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Off-the-shelf third-party HSC-engineered iNKT cells for ameliorating GvHD while preserving GvL effect in the treatment of blood cancers.iScience. 2022 Aug 6;25(9):104859. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104859. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36034226 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing cell-based cancer immunotherapy through stem cell engineering.Cell Stem Cell. 2023 May 4;30(5):592-610. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2023.02.009. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Cell Stem Cell. 2023. PMID: 36948187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

