The identification of alternative oxidase in intermediate host snails of Schistosoma and its potential role in protecting Oncomelania hupensis against niclosamide-induced stress
- PMID: 35313980
- PMCID: PMC8935807
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-022-05227-5
The identification of alternative oxidase in intermediate host snails of Schistosoma and its potential role in protecting Oncomelania hupensis against niclosamide-induced stress
Abstract
Background: Snail intermediate hosts are mandatory for the transmission of schistosomiasis, which has to date infected more than 200 million people worldwide. Our previous studies showed that niclosamide treatment caused the inhibition of aerobic respiration and oxidative phosphorylation, and the disruption of energy supply, in one of the intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis, Oncomelania hupensis, which eventually led to the death of the snails. Meanwhile, the terminal oxidase in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, alternative oxidase (AOX), was significantly up-regulated, which was thought to counterbalance the oxidative stress and maintain metabolic homeostasis in the snails. The aims of the present study are to identify the AOXs in several species of snails and investigate the potential activation of O. hupensis AOX (OhAOX) under niclosamide-induced stress, leading to enhanced survival of the snail when exposed to this molluscicide.
Methods: The complete complementary DNA was amplified from the AOXs of O. hupensis and three species of Biomphalaria; the sequence characteristics were analysed and the phylogenetics investigated. The dynamic expression and localisation of the AOX gene and protein in O. hupensis under niclosamide-induced stress were examined. In addition, the expression pattern of genes in the mitochondrial respiratory complex was determined and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) calculated. Finally, the molluscicidal effect of niclosamide was compared between snails with and without inhibition of AOX activity.
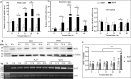
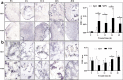
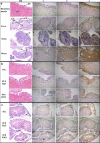
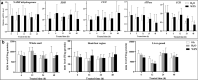
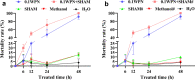
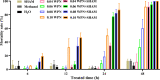
Results: AOXs containing the invertebrate AOX-specific motif NP-[YF]-XPG-[KQE] were identified from four species of snail, which phylogenetically clustered together into Gastropoda AOXs and further into Mollusca AOXs. After niclosamide treatment, the levels of OhAOX messenger RNA (mRNA) and OhAOX protein in the whole snail were 14.8 and 2.6 times those in untreated snails, respectively, but varied widely among tissues. Meanwhile, the level of cytochrome C reductase mRNA showed a significant decrease in the whole snail, and ROS production showed a significant decrease in the liver plus gonad (liver-gonad) of the snails. At 24 h post-treatment, the mortality of snails treated with 0.06-0.1 mg/L niclosamide and AOX inhibitor was 56.31-76.12% higher than that of snails treated with 0.1 mg/L niclosamide alone.
Conclusions: AOX was found in all the snail intermediate hosts of Schistosoma examined here. AOX was significantly activated in O. hupensis under niclosamide-induced stress, which led to a reduction in oxidative stress in the snail. The inhibition of AOX activity in snails can dramatically enhance the molluscicidal effect of niclosamide. A potential target for the development of an environmentally safe snail control method, which acts by inhibiting the activity of AOX, was identified in this study.
Keywords: Alternative oxidase; Intermediate host; Mitochondrial respiratory chain; Niclosamide; Oncomelania hupensis; Schistosoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of alternative oxidase disrupts the development and oviposition of Biomphalaria glabrata snails.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Feb 17;16(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05642-8. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 36804043 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic profiles of Oncomelania hupensis after molluscicidal treatment: Carbohydrate metabolism targeted and energy deficiency.Acta Trop. 2020 Oct;210:105580. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105580. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Acta Trop. 2020. PMID: 32533936
-
Sensitivity of Oncomelania hupensis to niclosamide: a nation-wide survey in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014 Mar 12;11(3):3086-95. doi: 10.3390/ijerph110303086. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014. PMID: 24625624 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the immune interactions between Oncomelania hupensis and Schistosoma japonicum, with a cross-comparison of immunological research progress in other intermediate host snails.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Dec 13;16(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06011-9. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 38093363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research progress on the molluscicidal effect of niclosamide compounded with other molluscicides against Oncomelania hupensis].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Feb;32(1):72-5. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24822372 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of alternative oxidase disrupts the development and oviposition of Biomphalaria glabrata snails.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Feb 17;16(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05642-8. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 36804043 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Oxidase: From Molecule and Function to Future Inhibitors.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 4;9(11):12478-12499. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c09339. eCollection 2024 Mar 19. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38524433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel insights into the glucose metabolic alterations of freshwater snails: a pathway to molluscicide innovation and snail control strategies.Parasitol Res. 2024 Jun 28;123(7):257. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08274-2. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 38940835 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

