Acute rhabdomyolysis in hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia patient undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: case report and literature review
- PMID: 35313994
- PMCID: PMC8935704
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-022-00675-2
Acute rhabdomyolysis in hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia patient undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia (HAAA) is a specific type of aplastic anemia, and hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is recommended as the first-line. Acute rhabdomyolysis (AR) during hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is a rare, serious complication, with only 10 cases reported in the world so far.
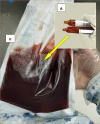
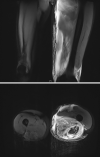
Case presentation: Herein, we present a case of AR developing during HLA-haploidentical HSCT in a 55-year-old man who suffered from HAAA. On day 7 after stem cell transfusion, the patient reported a muscle pull in thigh and complained of muscle swelling, pain and change in urine color. Despite the timely diagnosis (based on the levels of myoglobin and creatine kinase, and muscle MRI findings, etc.) and rapid hydration and alkalization, the situation progressed dramatically, and the patient died of multi-organ failure during the preparation for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). Five days after his death, the whole-exome sequencing result confirmed that the patient had a germline missense mutation in SCN4A I 1545 V and ACTN3 R577X.
Conclusion: AR is a rare but threatening complication during HSCT, especially in cases with kidney dysfunction. The creatine kinase level may not truly and completely reflect the severity and prognosis for cases with localized lesion. We suggest that genetic analysis should be performed for better understanding the pathological changes of AR during HSCT, especially for patients with bone marrow failure.
Keywords: Anemia, aplastic; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Hepatitis; Rhabdomyolysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 82174138/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81774092/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- LY17H290005/Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province
- 2020ZB085/Zhejiang Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Foundation
- JDZX2015109/Specialized Project for Scientific Research of Bases for TCM Clinical Research of State Administration of TCM
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

