Propagation of tau and α-synuclein in the brain: therapeutic potential of the glymphatic system
- PMID: 35314000
- PMCID: PMC8935752
- DOI: 10.1186/s40035-022-00293-2
Propagation of tau and α-synuclein in the brain: therapeutic potential of the glymphatic system
Abstract
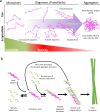
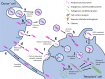
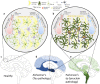
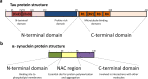
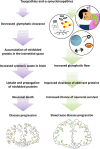
Many neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, are characterised by the accumulation of misfolded protein deposits in the brain, leading to a progressive destabilisation of the neuronal network and neuronal death. Among the proteins that can abnormally accumulate are tau and α-synuclein, which can propagate in a prion-like manner and which upon aggregation, represent the most common intracellular proteinaceous lesions associated with neurodegeneration. For years it was thought that these intracellular proteins and their accumulation had no immediate relationship with extracellular homeostasis pathways such as the glymphatic clearance system; however, mounting evidence has now suggested that this is not the case. The involvement of the glymphatic system in neurodegenerative disease is yet to be fully defined; however, it is becoming increasingly clear that this pathway contributes to parenchymal solute clearance. Importantly, recent data show that proteins prone to intracellular accumulation are subject to glymphatic clearance, suggesting that this system plays a key role in many neurological disorders. In this review, we provide a background on the biology of tau and α-synuclein and discuss the latest findings on the cell-to-cell propagation mechanisms of these proteins. Importantly, we discuss recent data demonstrating that manipulation of the glymphatic system may have the potential to alleviate and reduce pathogenic accumulation of propagation-prone intracellular cytotoxic proteins. Furthermore, we will allude to the latest potential therapeutic opportunities targeting the glymphatic system that might have an impact as disease modifiers in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Aquaporin-4; Clearance; Glymphatic; Propagation; Synucleinopathy; Tauopathy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

