Dynamics of specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients after recovery
- PMID: 35314019
- PMCID: PMC8987644
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268822000528
Dynamics of specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients after recovery
Abstract
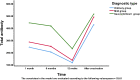
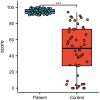
The ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to an unprecedented global public health crisis. The objectives of this study were to analyse the dynamic trend in specific antibodies in the serum of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 within 12 months after recovery and to make a preliminary assessment of the protective effect of vaccination. Eighty-seven patients with confirmed COVID-19 who were admitted to our hospital from January to February 2020 were followed after recovery. Three-millilitre blood samples were collected for specific antibody detection at four time points: 1, 6 and 12 months after recovery and 1 month after vaccination. The changes in specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody and total antibody levels over 12 months were analysed. Moreover, an independent comparison of the neutralising antibody levels of patients after vaccination with those of healthy medical staff after vaccination was performed to compare the inhibition rates of the neutralising antibody to the virus. No statistically significant difference in the sex distribution between groups was observed (P > 0.05). Older patients had a greater risk of developing severe and critical COVID-19 (P < 0.05). The percentages of subjects positive for IgG antibodies at 1, 6 and 12 months after recovery were 88.5%, 75.9% and 50.6%, respectively. The rate of IgG antibody conversion from positive to negative was not uniform across time points: the change was slow in the first 6 months but increased significantly in the last 6 months (P < 0.05). The positive rate of critically ill patients in the first 6 months was 100.0%. The trend over time in total antibody levels was similar to that of IgG antibody levels. Over 12 months, the sample/cut off value of total antibodies continued to decrease, while that of different disease severities was significantly different (P < 0.05). After vaccine administration, the total antibody level exceeded the detection level in the first month, which was independent of disease severity (P > 0.05). Significant differences were observed in the inhibition rate of the neutralising antibody against the virus in the disease group and the control group (P < 0.05). IgG antibody produced by patients naturally infected with SARS-CoV-2 has a duration of no less than 1 year, and the change trend graph of total antibody levels was the same as that of IgG antibody levels. Under vaccine stimulation, the positive rate of IgG antibody was as high as 100%, and the total antibody concentration reached the highest level, which was independent of disease severity. Neutralising antibodies following vaccination in patients who recovered from COVID-19 had a higher inhibition rate against SARS-CoV-2 than those of vaccinated healthy controls, indicating that these COVID-19 patients had a lower risk of reinfection and were better protected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamics of viral load and anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in patients with positive RT-PCR results after recovery from COVID-19.Korean J Intern Med. 2021 Jan;36(1):11-14. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2020.325. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Korean J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 32972123 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Specific and Neutralizing Antibodies over Seven Months after Symptom Onset in COVID-19 Patients.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0059021. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00590-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34550000 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies and neutralising antibodies in rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases patients with COVID-19.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2024 May;42(5):1035-1042. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/fpd8tj. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38372719
-
SARS-COV-2 IgG specific antibodies persistence in recovered COVID-19 individuals and its association with severity and time of illness.New Microbes New Infect. 2023 Mar;52:101096. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101096. Epub 2023 Feb 3. New Microbes New Infect. 2023. PMID: 36776158 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery scenario and immunity in COVID-19 disease: A new strategy to predict the potential of reinfection.J Adv Res. 2021 Jul;31:49-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.12.013. Epub 2021 Jan 5. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 33520309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous