Domain-selective BET inhibition attenuates transcriptional and behavioral responses to cocaine
- PMID: 35314160
- PMCID: PMC8986626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109040
Domain-selective BET inhibition attenuates transcriptional and behavioral responses to cocaine
Abstract
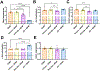
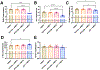
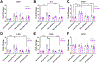
Epigenetic pharmacotherapies have emerged as a promising treatment option for substance use disorder (SUD) due to their ability to reverse maladaptive transcriptional and behavioral responses to drugs of abuse. In particular, inhibitors of bromodomain and extra terminal domain (BET) reader proteins have been shown to reduce cocaine- and opioid-seeking behaviors in rodents. However, only pan-BET inhibitors, small molecules that bind to both bromodomains (BD1 and BD2) with all BET proteins, have been investigated in animal models of SUD. Given the potential side effects associated with pan-BET inhibitors, safer and more selective strategies are needed to advance BET therapeutics as a potential treatment for SUD. Here, we show that RVX-208, a clinically tested, BD2-selective BET inhibitor, dose-dependently reduced cocaine conditioned place preference in male and female mice, similar to the pan-BET inhibitor JQ1. In other behavioral experiments, RVX-208 treatment did not alter distance traveled, anxiety-like behavior, or novel object recognition memory. At the transcriptional level, RVX-208 attenuated the expression of multiple cocaine-induced genes in the nucleus accumbens in a sex-dependent manner. RVX-208 produced a distinct transcriptional response in stimulated primary neurons compared to JQ1 but had little effect on gene expression in non-stimulated neurons. Together, these data indicate that targeting domain-specific BET mechanisms may be an effective and safer strategy to reduce cocaine-induced neurobehavioral adaptations.
Keywords: Addiction; BET; BRD4; Bromodomain; Cocaine; Epigenetics; Substance use disorder.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Readers of Lysine Acetylation Regulate Cocaine-Induced Plasticity.J Neurosci. 2015 Nov 11;35(45):15062-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0826-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26558777 Free PMC article.
-
RVX-297- a novel BD2 selective inhibitor of BET bromodomains.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Aug 12;477(1):62-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.021. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27282480
-
JQ1 attenuates psychostimulant- but not opioid-induced conditioned place preference.Behav Brain Res. 2022 Feb 10;418:113644. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113644. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Behav Brain Res. 2022. PMID: 34757001 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the development of domain selective inhibitors of the bromo and extra terminal domain family (BET) proteins.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Dec 15;226:113853. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113853. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34547507 Review.
-
BET bromodomains as novel epigenetic targets for brain health and disease.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Dec 15;181:108306. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108306. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32946883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Opioid Receptors by Drugs of Abuse.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 5;23(19):11804. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911804. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Proteins in Brain Physiology and Pathology: BET-ing on Epigenetic Regulation.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 1;11(3):750. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030750. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone modifications in cocaine, methamphetamine and opioids.Heliyon. 2023 May 19;9(6):e16407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16407. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37265630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine on oxycodone withdrawal and reinstatement.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023 Dec 1;253:110987. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.110987. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023. PMID: 37864957 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing withdrawal- and anxiety-like behaviors following oral and subcutaneous oxycodone administration in C57BL/6 mice.Behav Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 1;35(5):269-279. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000780. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Behav Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38847447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amorim S, Stathis A, Gleeson M, Iyengar S, Magarotto V, Leleu X, Morschhauser F, Karlin L, Broussais F, Rezai K, Herait P, Kahatt C, Lokiec F, Salles G, Facon T, Palumbo A, Cunningham D, Zucca E, Thieblemont C, 2016. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or multiple myeloma: a dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol 3, e196–204. 10.1016/S2352-3026(16)00021-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berthon C, Raffoux E, Thomas X, Vey N, Gomez-Roca C, Yee K, Taussig DC, Rezai K, Roumier C, Herait P, Kahatt C, Quesnel B, Michallet M, Recher C, Lokiec F, Preudhomme C, Dombret H, 2016. Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with acute leukaemia: A dose-escalation, phase 1 study. The Lancet Haematology 3, e186–e195. 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00247-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

