Degron tagging of BleoR and other antibiotic-resistance genes selects for higher expression of linked transgenes and improved exosome engineering
- PMID: 35314197
- PMCID: PMC9111990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101846
Degron tagging of BleoR and other antibiotic-resistance genes selects for higher expression of linked transgenes and improved exosome engineering
Abstract
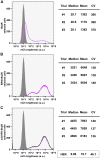
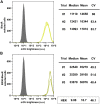
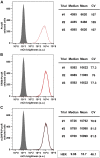
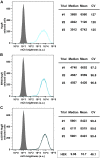
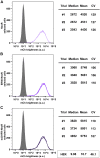
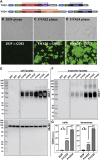
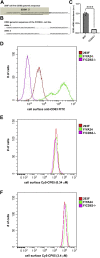
Five antibiotic resistance (AR) genes have been used to select for transgenic eukaryotic cell lines, with the BleoR, PuroR, HygR, NeoR, and BsdR cassettes conferring resistance to zeocin, puromycin, hygromycin, geneticin/G418, and blasticidin, respectively. We recently demonstrated that each AR gene establishes a distinct threshold of transgene expression below which no cell can survive, with BleoR selecting for the highest level of transgene expression, nearly ∼10-fold higher than in cells selected using the NeoR or BsdR markers. Here, we tested the hypothesis that there may be an inverse proportionality between AR protein function and the expression of linked, transgene-encoded, recombinant proteins. Specifically, we fused each AR protein to proteasome-targeting degron tags, used these to select for antibiotic-resistant cell lines, and then measured the expression of the linked, recombinant protein, mCherry, as a proxy marker of transgene expression. In each case, degron-tagged AR proteins selected for higher mCherry expression than their cognate WT AR proteins. ER50BleoR selected for the highest level of mCherry expression, greater than twofold higher than BleoR or any other AR gene. Interestingly, use of ER50BleoR as the selectable marker translated to an even higher, 3.5-fold increase in the exosomal loading of the exosomal cargo protein, CD63/Y235A. Although a putative CD63-binding peptide, CP05, has been used to decorate exosome membranes in a technology known as "exosome painting," we show here that CP05 binds equally well to CD63-/- cells, WT 293F cells, and CD63-overexpressing cells, indicating that CP05 may bind membranes nonspecifically. These results are of high significance for cell engineering and especially for exosome engineering.
Keywords: CD63; G418; antibiotic; blasticidin; extracellular vesicle; hygromycin; puromycin; selectable marker; transgenic; zeocin.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest S. J. G. is a paid consultant for Capricor, holds equity in Capricor, and is coinventor of intellectual property licensed by Capricor. S. J. T. and C. G. are coinventors of intellectual property licensed by Capricor. Y.I. declares that he has no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Choice of selectable marker affects recombinant protein expression in cells and exosomes.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul;297(1):100838. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100838. Epub 2021 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34051235 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the optimal concentration of several selective drugs useful for generating multi-transgenic porcine embryonic fibroblasts.Reprod Domest Anim. 2012 Oct;47(5):759-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2011.01964.x. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Reprod Domest Anim. 2012. PMID: 22136322
-
Sequential deletion of CD63 identifies topologically distinct scaffolds for surface engineering of exosomes in living human cells.Nanoscale. 2020 Jun 11;12(22):12014-12026. doi: 10.1039/d0nr00362j. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32463402 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in development of marker-free transgenic plants: regulation and biosafety concern.J Biosci. 2012 Mar;37(1):167-97. doi: 10.1007/s12038-012-9187-5. J Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22357214 Review.
-
Transient and stable vector transfection: Pitfalls, off-target effects, artifacts.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017 Jul;773:91-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 16. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28927539 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocytosis blocks the vesicular secretion of exosome marker proteins.Sci Adv. 2024 May 10;10(19):eadi9156. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi9156. Epub 2024 May 8. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38718108 Free PMC article.
-
Exomap1 mouse: A transgenic model for in vivo studies of exosome biology.Extracell Vesicle. 2023 Dec;2:100030. doi: 10.1016/j.vesic.2023.100030. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Extracell Vesicle. 2023. PMID: 39372847 Free PMC article.
-
Antigen-display exosomes provide adjuvant-free protection against SARS-CoV-2 disease at nanogram levels of spike protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 5:2024.01.04.574272. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.04.574272. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38328234 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Protein expression/secretion boost by a novel unique 21-mer cis-regulatory motif (Exin21) via mRNA stabilization.Mol Ther. 2023 Apr 5;31(4):1136-1158. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.02.012. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36793212 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Method for Primary Blood Cell Culturing and Selection in Drosophila melanogaster.Cells. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):24. doi: 10.3390/cells12010024. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mulligan R.C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980;209:1422–1427. - PubMed
-
- Dhara V.G., Naik H.M., Majewska N.I., Betenbaugh M.J. Recombinant antibody production in CHO and NS0 cells: Differences and similarities. BioDrugs. 2018;32:571–584. - PubMed
-
- Ghilardi N., Pappu R., Arron J.R., Chan A.C. 30 Years of biotherapeutics development-what have we learned? Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020;38:249–287. - PubMed
-
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Hasler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985;41:521–530. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca J.P., Bonny A.R., Kumar G.R., Ng A.H., Town J., Wu Q.C., Aslankoohi E., Chen S.Y., Dods G., Harrigan P., Osimiri L.C., Kistler A.L., El-Samad H. A toolkit for rapid modular construction of biological circuits in mammalian cells. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019;8:2593–2606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

