Acute Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Exendin-4 in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 35314564
- PMCID: PMC9899697
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.60921
Acute Cholesterol-Lowering Effect of Exendin-4 in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
Aims: We previously reported that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) reduced serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving statins, which increased LDL receptor (LDLR) expression. Nevertheless, it remains unclear how much LDLR expression contributes to the LDL-C-lowering effect of GLP-1RAs. We examined the effect of a GLP-1RA, namely, exendin-4, on serum LDL-C levels and its mechanism in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J mice.
Methods: Ten-week-old Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J mice received exendin-4 or saline for 5 days, and serum lipid profiles and hepatic lipid levels were examined. Cholesterol metabolism-related gene expression and protein levels in the liver and ileum and the fecal bile acid (BA) composition were also examined.
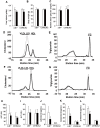
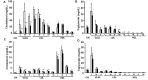
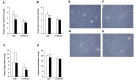
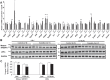
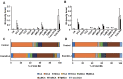
Results: Exendin-4 treatment significantly decreased serum very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-C) and LDL-C levels and mature hepatic SREBP2 levels and increased hepatic Insig1/2 mRNA expression in both mouse strains. In Ldlr-/- mice, exendin-4 treatment also significantly decreased hepatic cholesterol levels and fecal BA excretion, decreased hepatic Cyp7a1 mRNA expression, and increased small intestinal Fgf15 mRNA expression. In C57BL/6J mice, exendin-4 treatment significantly decreased small intestinal NPC1L1 levels.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that exendin-4 treatment decreased serum VLDL-C and LDL-C levels in a manner that was independent of LDLR. Exendin-4 treatment might decrease serum cholesterol levels by lowering hepatic SREBP2 levels and cholesterol absorption in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J mice. Exendin-4 treatment might decrease cholesterol absorption by different mechanisms in Ldlr-/- and C57BL/6J mice.
Keywords: Cholesterol absorption; GLP-1 receptor agonist; LDL-cholesterol; Ldlr-deficient mice; SREBP2; VLDL-cholesterol.
Figures
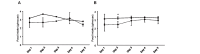

References
-
- MacDonald PE, El-Kholy W, Riedel MJ, Salapatek AM, Light PE and Wheeler MB: The multiple actions of GLP-1 on the process of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes, 2002; 51 Suppl 3: S434-442 - PubMed
-
- Yamato E, Noma Y, Tahara Y, Ikegami H, Yamamoto Y, Cha T, Yoneda H, Ogihara T, Ohboshi C, Hirota M and Shima K: Suppression of synthesis and release of glucagon by glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36 amide) without affect on mRNA level in isolated rat islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1990; 167: 431-437 - PubMed
-
- Viswanathan P, Chaudhuri A, Bhatia R, Al-Atrash F, Mohanty P and Dandona P: Exenatide therapy in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin. Endocr Pract, 2007; 13: 444-450 - PubMed
-
- Klonoff DC, Buse JB, Nielsen LL, Guan X, Bowlus CL, Holcombe JH, Wintle ME and Maggs DG: Exenatide effects on diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular risk factors and hepatic biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes treated for at least 3 years. Curr Med Res Opin, 2008; 24: 275-286 - PubMed

