Final Report on Clinical Outcomes and Tumor Recurrence Patterns of a Pilot Study Assessing Efficacy of Belinostat (PXD-101) with Chemoradiation for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
- PMID: 35314634
- PMCID: PMC8938806
- DOI: 10.3390/tomography8020057
Final Report on Clinical Outcomes and Tumor Recurrence Patterns of a Pilot Study Assessing Efficacy of Belinostat (PXD-101) with Chemoradiation for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma
Abstract
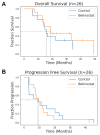
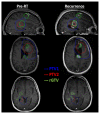
Glioblastoma (GBM) is highly aggressive and has a poor prognosis. Belinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor with blood-brain barrier permeability, anti-GBM activity, and the potential to enhance chemoradiation. The purpose of this clinical trial was to assess the efficacy of combining belinostat with standard-of-care therapy. Thirteen patients were enrolled in each of control and belinostat cohorts. The belinostat cohort was given a belinostat regimen (500-750 mg/m2 1×/day × 5 days) every three weeks (weeks 0, 3, and 6 of RT). All patients received temozolomide and radiation therapy (RT). RT margins of 5-10 mm were added to generate clinical tumor volumes and 3 mm added to create planning target volumes. Median overall survival (OS) was 15.8 months for the control cohort and 18.5 months for the belinostat cohort (p = 0.53). The recurrence volumes (rGTVs) for the control cohort occurred in areas that received higher radiation doses than that in the belinostat cohort. For those belinostat patients who experienced out-of-field recurrence, tumors were detectable by spectroscopic MRI before RT. Recurrence analysis suggests better in-field control with belinostat. This study highlights the potential of belinostat as a synergistic therapeutic agent for GBM. It may be particularly beneficial to combine this radio-sensitizing effect with spectroscopic MRI-guided RT.
Keywords: epigenetic drug; glioblastoma; histone deacetylase; magnetic resonance spectroscopy; radiation sensitizer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R., Hegi M.E., Mason W.P., van den Bent M.J., Taphoorn M.J., Janzer R.C., Ludwin S.K., Allgeier A., Fisher B., Belanger K., et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R., Taillibert S., Kanner A., Read W., Steinberg D., Lhermitte B., Toms S., Idbaih A., Ahluwalia M.S., Fink K., et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;318:2306–2316. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.18718. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gondi V., Pugh S., Tsien C., Chenevert T., Gilbert M., Omuro A., Mcdonough J., Aldape K., Srinivasan A., Rogers C., et al. Radiotherapy (RT) Dose-intensification (DI) Using Intensity-modulated RT (IMRT) versus Standard-dose (SD) RT with Temozolomide (TMZ) in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma (GBM): Preliminary Results of NRG Oncology BN001. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020;108:S22–S23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.07.2109. - DOI
-
- Stupp R., Taillibert S., Kanner A.A., Kesari S., Steinberg D.M., Toms S.A., Taylor L.P., Lieberman F., Silvani A., Fink K.L., et al. Maintenance Therapy With Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Temozolomide vs Temozolomide Alone for Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2015;314:2535–2543. doi: 10.1001/jama.2015.16669. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

