EDNC: Ensemble Deep Neural Network for COVID-19 Recognition
- PMID: 35314648
- PMCID: PMC8938826
- DOI: 10.3390/tomography8020071
EDNC: Ensemble Deep Neural Network for COVID-19 Recognition
Abstract
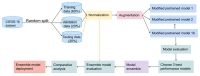
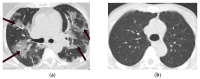
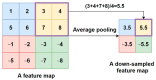
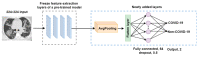
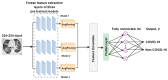
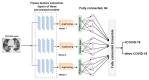
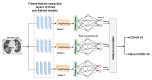
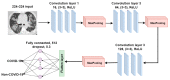
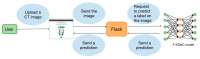
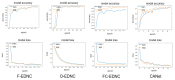
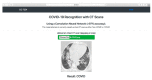
The automatic recognition of COVID-19 diseases is critical in the present pandemic since it relieves healthcare staff of the burden of screening for infection with COVID-19. Previous studies have proven that deep learning algorithms can be utilized to aid in the diagnosis of patients with potential COVID-19 infection. However, the accuracy of current COVID-19 recognition models is relatively low. Motivated by this fact, we propose three deep learning architectures, F-EDNC, FC-EDNC, and O-EDNC, to quickly and accurately detect COVID-19 infections from chest computed tomography (CT) images. Sixteen deep learning neural networks have been modified and trained to recognize COVID-19 patients using transfer learning and 2458 CT chest images. The proposed EDNC has then been developed using three of sixteen modified pre-trained models to improve the performance of COVID-19 recognition. The results suggested that the F-EDNC method significantly enhanced the recognition of COVID-19 infections with 97.75% accuracy, followed by FC-EDNC and O-EDNC (97.55% and 96.12%, respectively), which is superior to most of the current COVID-19 recognition models. Furthermore, a localhost web application has been built that enables users to easily upload their chest CT scans and obtain their COVID-19 results automatically. This accurate, fast, and automatic COVID-19 recognition system will relieve the stress of medical professionals for screening COVID-19 infections.
Keywords: COVID-19; CT scans; automatic recognition; deep learning; ensemble; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Automated detection of COVID-19 using ensemble of transfer learning with deep convolutional neural network based on CT scans.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Jan;16(1):115-123. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02286-w. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33191476 Free PMC article.
-
Classifying chest CT images as COVID-19 positive/negative using a convolutional neural network ensemble model and uniform experimental design method.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Nov 8;22(Suppl 5):147. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04083-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34749629 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Recognition Using Ensemble-CNNs in Two New Chest X-ray Databases.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 3;21(5):1742. doi: 10.3390/s21051742. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802428 Free PMC article.
-
Utilisation of deep learning for COVID-19 diagnosis.Clin Radiol. 2023 Feb;78(2):150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2022.11.006. Clin Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36639173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Learning in the Detection and Diagnosis of COVID-19 Using Radiology Modalities: A Systematic Review.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Mar 15;2021:6677314. doi: 10.1155/2021/6677314. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 33747419 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Uncertain-CAM: Uncertainty-Based Ensemble Machine Voting for Improved COVID-19 CXR Classification and Explainability.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 26;13(3):441. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030441. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766546 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on Deep Structured Learning for COVID-19 Screening Using Chest CT from 2020 to 2022.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;11(17):2388. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11172388. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Convolutional Neural Networks and Transformers for the Classification of Images of COVID-19, Pneumonia and Healthy Individuals as Observed with Computed Tomography.J Imaging. 2022 Sep 1;8(9):237. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8090237. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36135403 Free PMC article.
-
A COVID-19 medical image classification algorithm based on Transformer.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 1;13(1):5359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32462-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37005476 Free PMC article.
-
Ensemble Deep Learning Derived from Transfer Learning for Classification of COVID-19 Patients on Hybrid Deep-Learning-Based Lung Segmentation: A Data Augmentation and Balancing Framework.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;13(11):1954. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111954. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 20 August 2021)]. Available online: https://Covid19.who.int.
-
- MRT The WHO Believes That We Have Already Traveled “60% of the Way” in the Fight against COVID-19. [(accessed on 11 October 2021)]. Available online: https://marketresearchtelecast.com/the-who-believes-that-we-have-already....
-
- Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19-31 August 2021. [(accessed on 1 September 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
-
- Sanderson K. COVID Vaccines Protect against Delta, but Their Effectiveness Wanes. [(accessed on 11 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-021-02261-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

