Thioredoxin interacting protein protects mice from fasting induced liver steatosis by activating ER stress and its downstream signaling pathways
- PMID: 35314758
- PMCID: PMC8938456
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08791-z
Thioredoxin interacting protein protects mice from fasting induced liver steatosis by activating ER stress and its downstream signaling pathways
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Thioredoxin interacting protein protects mice from fasting induced liver steatosis by activating ER stress and its downstream signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2022 May 16;12(1):8026. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11823-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35577819 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
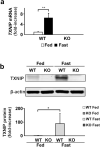
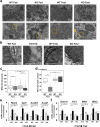
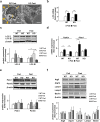
Under normal conditions, fasting results in decreased protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) activity and accumulation of unfolded proteins, leading to the subsequent activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR)/autophagy signaling pathway to eliminate damaged mitochondria. Fasting also induces upregulation of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) expression and mice deficient of this protein (TXNIP-KO mice) was shown to develop severe hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia and liver steatosis (LS). In the present study, we aimed to determine the role of TXNIP in fasting-induced LS by using male TXNIP-KO mice that developed LS without severe hypoglycemia. In TXNIP-KO mice, fasting induced severe microvesicular LS. Examinations by transmission electron microscopy revealed mitochondria with smaller size and deformities and the presence of few autophagosomes. The expression of β-oxidation-associated genes remained at the same level and the level of LC3-II was low. PDI activity level stayed at the original level and the levels of p-IRE1 and X-box binding protein 1 spliced form (sXBP1) were lower. Interestingly, treatment of TXNIP-KO mice with bacitracin, a PDI inhibitor, restored the level of LC3-II after fasting. These results suggest that TXNIP regulates PDI activity and subsequent activation of the UPR/autophagy pathway and plays a protective role in fasting-induced LS.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang H, et al. The role of mitochondria in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury: From aspects of mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial fission, mitochondrial membrane permeable transport pore formation, mitophagy, and mitochondria-related protective measures. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021;2021:6670579. doi: 10.1155/2021/6670579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

