Isoeugenol affects expression pattern of conidial hydrophobin gene RodA and transcriptional regulators MedA and SomA responsible for adherence and biofilm formation in Aspergillus fumigatus
- PMID: 35314887
- PMCID: PMC8938220
- DOI: 10.1007/s00203-022-02817-w
Isoeugenol affects expression pattern of conidial hydrophobin gene RodA and transcriptional regulators MedA and SomA responsible for adherence and biofilm formation in Aspergillus fumigatus
Abstract
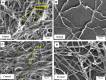
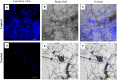
Aspergillus fumigatus is one of the major pathogenic fungal species, causing life-threatening infections. Due to a limited spectrum of available antifungals, exploration of new drug targets as well as potential antifungal molecules has become pertinent. Rodlet layer plays an important role in adherence of fungal conidia to hydrophobic cell surfaces in host, which also leads to A. fumigatus biofilm formation, contributing factor to fungal pathogenicity. From decades, natural sources have been known for the development of new active molecules. The present study investigates effect of isoeugenol on genes responsible for hydrophobins (RodA), adhesion as well as biofilm formation (MedA and SomA) of A. fumigatus. Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC and IC50) of isoeugenol against A. fumigatus were determined using broth microdilution assay. The IC50 results showed reduced hydrophobicity and biofilm formation as well as eradication after treatment with the compound and electron micrograph data corroborated these findings. The qRT-PCR showed a significant downregulation of genes RodA, MedA, SomA and pksP involved in hydrophobicity and biofilm formation. SwissADME studies potentiated drug-like propensity for isoeugenol which formed four hydrogen bonds with low binding energy (- 4.54 kcal/mol) at the catalytic site of RodA protein studied via AutoDock4. Hence, the findings conclude that isoeugenol inhibits conidial hydrophobicity and biofilm formation of A. fumigatus and further investigations are warranted in this direction.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Hydrophobicity; Isoeugenol; Transcription regulators; Virulence.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors. The authors are responsible for the content and paper writing.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Protein disulfide isomerase 1 is required for RodA assembling-based conidial hydrophobicity of Aspergillus fumigatus.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Apr 17;90(4):e0126023. doi: 10.1128/aem.01260-23. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38501925 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome Analysis Reveals the Conidial Surface Protein CcpA Essential for Virulence of the Pathogenic Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus.mBio. 2018 Oct 2;9(5):e01557-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01557-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30279286 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hydrophobins in Aspergillus fumigatus.J Fungi (Basel). 2017 Dec 24;4(1):2. doi: 10.3390/jof4010002. J Fungi (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29371496 Free PMC article.
-
Genes and molecules involved in Aspergillus fumigatus virulence.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2005 Mar;22(1):1-23. doi: 10.1016/s1130-1406(05)70001-2. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2005. PMID: 15813678 Review.
-
MybA, a new player driving survival of the conidium of the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):141-146. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0740-5. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28840304 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the osaA Gene in Aspergillus fumigatus Development, Secondary Metabolism and Virulence.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jan 26;10(2):103. doi: 10.3390/jof10020103. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392775 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of eugenol/isoeugenol glycoconjugates and other analogues as antifungal agents against Aspergillus fumigatus.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Jun 2;13(8):955-962. doi: 10.1039/d2md00138a. eCollection 2022 Aug 17. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36092146 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics studies to identify potential antifungal compounds targeting virulence proteins/genes VelB and THR as possible drug targets against Curvularia lunata.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 12;9:1055945. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1055945. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36619165 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus Hydrophobins: Physicochemical Properties, Biochemical Properties, and Functions in Solid Polymer Degradation.Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 25;10(8):1498. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10081498. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35893556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cyp51A mutations, protein modeling, and efflux pump gene expression reveals multifactorial complexity towards understanding Aspergillus section Nigri azole resistance mechanism.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;14(1):6156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55237-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38486086 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

