Effects of Polyphenols on Glucose-Induced Metabolic Changes in Healthy Human Subjects and on Glucose Transporters
- PMID: 35315210
- PMCID: PMC9788283
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.202101113
Effects of Polyphenols on Glucose-Induced Metabolic Changes in Healthy Human Subjects and on Glucose Transporters
Abstract
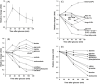
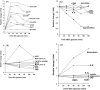
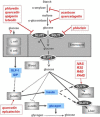
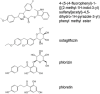
Dietary polyphenols interact with glucose transporters in the small intestine and modulate glucose uptake after food or beverage consumption. This review assesses the transporter interaction in vitro and how this translates to an effect in healthy volunteers consuming glucose. As examples, the apple polyphenol phlorizin inhibits sodium-glucose linked transporter-1; in the intestinal lumen, it is converted to phloretin, a strong inhibitor of glucose transporter-2 (GLUT2), by the brush border digestive enzyme lactase. Consequently, an apple extract rich in phlorizin attenuates blood glucose and insulin in healthy volunteers after a glucose challenge. On the other hand, the olive phenolic, oleuropein, inhibits GLUT2, but the strength of the inhibition is not enough to modulate blood glucose after a glucose challenge in healthy volunteers. Multiple metabolic effects and oxidative stresses after glucose consumption include insulin, incretin hormones, fatty acids, amino acids, and protein markers. However, apart from acute postprandial effects on glucose, insulin, and some incretin hormones, very little is known about the acute effects of polyphenols on these glucose-induced secondary effects. In summary, attenuation of the effect of a glucose challenge in vivo is only observed when polyphenols are strong inhibitors of glucose transporters.
Keywords: OGTT; dihydrochalcone; flavonoid; insulin; post prandial; sugar.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of the intestinal sodium-coupled glucose transporter 1 (SGLT1) by extracts and polyphenols from apple reduces postprandial blood glucose levels in mice and humans.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014 Sep;58(9):1795-808. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201400016. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2014. PMID: 25074384 Clinical Trial.
-
Apple polyphenol-rich drinks dose-dependently decrease early-phase postprandial glucose concentrations following a high-carbohydrate meal: a randomized controlled trial in healthy adults and in vitro studies.J Nutr Biochem. 2020 Nov;85:108466. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108466. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32739411 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute anti-hyperglycaemic effects of an unripe apple preparation containing phlorizin in healthy volunteers: a preliminary study.J Sci Food Agric. 2015 Feb;95(3):560-8. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6779. Epub 2014 Jul 4. J Sci Food Agric. 2015. PMID: 24917557 Clinical Trial.
-
Natural Products as Lead Compounds for Sodium Glucose Cotransporter (SGLT) Inhibitors.Planta Med. 2017 Aug;83(12-13):985-993. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-106050. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Planta Med. 2017. PMID: 28395363 Review.
-
Possible effects of dietary polyphenols on sugar absorption and digestion.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Jan;57(1):48-57. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200511. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013. PMID: 23180627 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted metabolomics unravels the mechanism by phenylpropanoid-rich of the peel of Zea mays L. ameliorates metabolic disorders in diabetic mice through gut microbiota modulation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1551713. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1551713. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40271058 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl Acetate Fractions of Tectona Grandis Crude Extract Modulate Glucose Absorption and Uptake as Well as Antihyperglycemic Potential in Fructose-Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 19;25(1):28. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010028. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203195 Free PMC article.
-
Small Phenolic Metabolites at the Nexus of Nutrient Transport and Energy Metabolism.Molecules. 2025 Feb 24;30(5):1026. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051026. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hypoglycaemic Effects of the New Zealand Pine Bark Extract on Sucrose Uptake and Glycaemic Responses in Healthy Adults-A Single-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 9;17(14):2277. doi: 10.3390/nu17142277. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40732901 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nanoplastics Toxicity Specific to Liver in Inducing Metabolic Dysfunction-A Comprehensive Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 26;14(3):590. doi: 10.3390/genes14030590. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Melchionda N., Forlani G., Marchesini G., Baraldi L., Natale S., Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 90. - PubMed
-
- Standardization of the oral glucose tolerance test, Diabetes 1969, 18, 299. - PubMed
-
- Bartoli E., Fra G. P., Carnevale Schianca P. G., Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 22, 8. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda M., DeFronzo R. A., Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1462. - PubMed
-
- Donga E., Dekkers O. M., Corssmit E. P., Romijn J. A., Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

