Decoding the Mechanism of Specific RNA Targeting by Ribosomal Methyltransferases
- PMID: 35316014
- PMCID: PMC7617139
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00732
Decoding the Mechanism of Specific RNA Targeting by Ribosomal Methyltransferases
Abstract
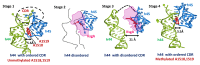
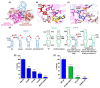
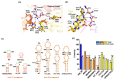
Methylation of specific nucleotides is integral for ribosomal biogenesis and also serves as a common mechanism to confer antibiotic resistance by pathogenic bacteria. Here, by determining the high-resolution structure of the 30S-KsgA complex by cryo-electron microscopy, a state was captured, where KsgA juxtaposes between helices h44 and h45 of the 30S ribosome, separating them, thereby enabling remodeling of the surrounded rRNA and allowing the cognate site to enter the methylation pocket. With the structure as a guide, several mutant versions of the ribosomes, where interacting bases in the catalytic helix h45 and surrounding helices h44, h24, and h27, were mutated and evaluated for their methylation efficiency revealing factors that direct the enzyme to its cognate site with high fidelity. The biochemical studies show that the three-dimensional environment of the ribosome enables the interaction of select loop regions in KsgA with the ribosome helices paramount to maintain selectivity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structural insights into methyltransferase KsgA function in 30S ribosomal subunit biogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10453-10459. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.318121. Epub 2012 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22308031 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutants of 16S rRNA reveal important RNA domains for KsgA function and 30S subunit assembly.Biochemistry. 2011 Feb 8;50(5):854-63. doi: 10.1021/bi101005r. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21142019 Free PMC article.
-
30S subunit recognition and G1405 modification by the aminoglycoside-resistance 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase RmtC.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 20;120(25):e2304128120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2304128120. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37307464 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-function correlations (and discrepancies) in the 16S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli.Biochimie. 1992 Apr;74(4):319-26. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90109-r. Biochimie. 1992. PMID: 1379076 Review.
-
Structural and evolutionary insights into ribosomal RNA methylation.Nat Chem Biol. 2018 Feb 14;14(3):226-235. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2569. Nat Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29443970 Review.
Cited by
-
Complete list of canonical post-transcriptional modifications in the Bacillus subtilis ribosome and their link to RbgA driven large subunit assembly.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 11:2024.05.10.593627. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.10.593627. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):11203-11217. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae626. PMID: 38765983 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Two dynamic N-terminal regions are required for function in ribosomal RNA adenine dimethylase family members.RNA. 2025 Jan 22;31(2):164-180. doi: 10.1261/rna.080068.124. RNA. 2025. PMID: 39516040
-
Miniature RNAs are embedded in an exceptionally protein-rich mitoribosome via an elaborate assembly pathway.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 7;51(12):6443-6460. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad422. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37207340 Free PMC article.
-
30S subunit recognition and G1405 modification by the aminoglycoside-resistance 16S ribosomal RNA methyltransferase RmtC.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 30:2023.03.13.532395. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.13.532395. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 20;120(25):e2304128120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2304128120. PMID: 36993224 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Complete list of canonical post-transcriptional modifications in the Bacillus subtilis ribosome and their link to RbgA driven large subunit assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):11203-11217. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae626. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39036956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson DN. Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Arenz S, Wilson DN. Blast from the Past: Reassessing Forgotten Translation Inhibitors, Antibiotic Selectivity, and Resistance Mechanisms to Aid Drug Development. Mol Cell. 2016;61:3–14. - PubMed
-
- Blair JMA, Webber MA, Baylay AJ, Ogbolu DO, Piddock LJV. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Alekshun MN, Levy SB. Molecular mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell. 2007;128:1037–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

