Programmable Cell-Free Transcriptional Switches for Antibody Detection
- PMID: 35316049
- PMCID: PMC8990998
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c11706
Programmable Cell-Free Transcriptional Switches for Antibody Detection
Abstract
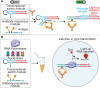
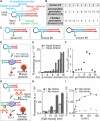
We report here the development of a cell-free in vitro transcription system for the detection of specific target antibodies. The approach is based on the use of programmable antigen-conjugated DNA-based conformational switches that, upon binding to a target antibody, can trigger the cell-free transcription of a light-up fluorescence-activating RNA aptamer. The system couples the unique programmability and responsiveness of DNA-based systems with the specificity and sensitivity offered by in vitro genetic circuitries and commercially available transcription kits. We demonstrate that cell-free transcriptional switches can efficiently measure antibody levels directly in blood serum. Thanks to the programmable nature of the sensing platform, the method can be adapted to different antibodies: we demonstrate here the sensitive, rapid, and cost-effective detection of three different antibodies and the possible use of this approach for the simultaneous detection of two antibodies in the same solution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generalizable Molecular Switch Designs for In Vivo Continuous Biosensing.Acc Chem Res. 2025 Mar 4;58(5):703-713. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.4c00721. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Acc Chem Res. 2025. PMID: 39954262 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Reaction-Assisted Programmable Transcriptional Switches for Bioactive Molecule Detection.Anal Chem. 2024 Jan 9;96(1):331-338. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04198. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38127443
-
Aptamer-Antibody Chimera Sensors for Sensitive, Rapid, and Reversible Molecular Detection in Complex Samples.ACS Sens. 2024 Mar 22;9(3):1168-1177. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c01638. Epub 2024 Feb 26. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 38407035
-
Replacing antibodies with aptamers in lateral flow immunoassay.Biosens Bioelectron. 2015 Sep 15;71:230-242. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.04.041. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015. PMID: 25912679 Review.
-
Synthetic Antigen-Conjugated DNA Systems for Antibody Detection and Characterization.ACS Sens. 2023 Jul 28;8(7):2415-2426. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c00564. Epub 2023 Jul 18. ACS Sens. 2023. PMID: 37463359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Programmable DNA-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering.Fundam Res. 2025 Jan 2;5(4):1384-1400. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2024.12.015. eCollection 2025 Jul. Fundam Res. 2025. PMID: 40777770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Smart nanomaterials for biosensing and therapy applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 17;11:1137508. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1137508. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36733966 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
DNA-based customized functional modules for signal transformation.Front Chem. 2023 Feb 14;11:1140022. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1140022. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36864900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular single-stranded DNA as a programmable vector for gene regulation in cell-free protein expression systems.Nat Commun. 2024 May 31;15(1):4635. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49021-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38821953 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial biosensors for diagnostics, surveillance and epidemiology: Today's achievements and tomorrow's prospects.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70047. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70047. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39548716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Z.; Yi Y.; Luo X.; Xiong N.; Liu Y.; Li S.; Sun R.; Wang Y.; Hu B.; Chen W.; Zhang Y.; Wang J.; Huang B.; Lin Y.; Yang J.; Cai W.; Wang X.; Cheng J.; Chen Z.; Sun K.; Pan W.; Zhan Z.; Chen L.; Ye F. Development and Clinical Application of a Rapid IgM-IgG Combined Antibody Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection Diagnosis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1518–1524. 10.1002/jmv.25727. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pardee K.; Green A. A.; Takahashi M. K.; Braff D.; Lambert G.; Lee J. W.; Ferrante T.; Ma D.; Donghia N.; Fan M.; Daringer N. M.; Bosch I.; Dudley D. M.; O’Connor D. H.; Gehrke L.; Collins J. J. Rapid, Low-Cost Detection of Zika Virus Using Programmable Biomolecular Components. Cell 2016, 165, 1255–1266. 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.059. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

