Biased agonists of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 differentially signal through Gαi:β-arrestin complexes
- PMID: 35316095
- PMCID: PMC9890572
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.abg5203
Biased agonists of the chemokine receptor CXCR3 differentially signal through Gαi:β-arrestin complexes
Abstract
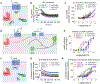
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of cell surface receptors and signal through the proximal effectors, G proteins and β-arrestins, to influence nearly every biological process. The G protein and β-arrestin signaling pathways have largely been considered separable; however, direct interactions between Gα proteins and β-arrestins have been described that appear to be part of a distinct GPCR signaling pathway. Within these complexes, Gαi/o, but not other Gα protein subtypes, directly interacts with β-arrestin, regardless of the canonical Gα protein that is coupled to the GPCR. Here, we report that the endogenous biased chemokine agonists of CXCR3 (CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11), together with two small-molecule biased agonists, differentially formed Gαi:β-arrestin complexes. Formation of the Gαi:β-arrestin complexes did not correlate well with either G protein activation or β-arrestin recruitment. β-arrestin biosensors demonstrated that ligands that promoted Gαi:β-arrestin complex formation generated similar β-arrestin conformations. We also found that Gαi:β-arrestin complexes did not couple to the mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK, as is observed with other receptors such as the V2 vasopressin receptor, but did couple with the clathrin adaptor protein AP-2, which suggests context-dependent signaling by these complexes. These findings reinforce the notion that Gαi:β-arrestin complex formation is a distinct GPCR signaling pathway and enhance our understanding of the spectrum of biased agonism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

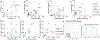
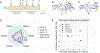



References
-
- Hamm HE, The many faces of G protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem 273, 669–672 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Manglik A, Lin H, Aryal DK, McCorvy JD, Dengler D, Corder G, Levit A, Kling RC, Bernat V, Hübner H, Huang X-P, Sassano MF, Giguère PM, Löber S, Duan D, Scherrer G, Kobilka BK, Gmeiner P, Roth BL, Shoichet BK, Structure-based discovery of opioid analgesics with reduced side effects. Nature 537, 185–190 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cahill TJ, Thomsen ARB, Tarrasch JT, Plouffe B, Nguyen AH, Yang F, Huang L-Y, Kahsai AW, Bassoni DL, Gavino BJ, Lamerdin JE, Triest S, Shukla AK, Berger B, Little J, Antar A, Blanc A, Qu C-X, Chen X, Kawakami K, Inoue A, Aoki J, Steyaert J, Sun J-P, Bouvier M, Skiniotis G, Lefkowitz RJ, Distinct conformations of GPCR-β-arrestin complexes mediate desensitization, signaling, and endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 114, 2562–2567 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

