NEDD4L inhibits glycolysis and proliferation of cancer cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma by inducing ENO1 ubiquitination and degradation
- PMID: 35316145
- PMCID: PMC8942561
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2022.2054244
NEDD4L inhibits glycolysis and proliferation of cancer cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma by inducing ENO1 ubiquitination and degradation
Abstract
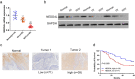
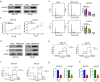
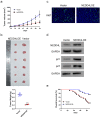
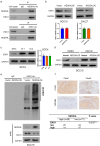
Glycolysis contributes to cell metabolism and facilitates cell proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), the most common type of oral cancer. Understanding the regulatory mechanisms involved in the glycolysis of OSCC cells may provide important therapeutic inspirations. Immunohistochemistry was used to examine protein localization patterns in human OSCC tissues and Western blot was conducted to gauge protein level. Lentivirus transduction was used to overexpress or silence genes of interest. Cell proliferation was assessed by Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assay while glycolysis was examined via measurement of extracellular acidification rate, oxygen consumption rate, and lactate and ATP production. In vivo cancer development was evaluated with a mouse tumor growth model. OSCC tissues displayed reduced expression of NEDD4L compared with normal tissues. NEDD4L expression positively correlated with 5-year patient survival rate, indicating that NEDD4L may be a prognosis marker for OSCC. NEDD4L overexpression suppressed proliferation, cell cycle transition, and glycolysis in OSCC cells, and inhibited in vivo tumor growth. UbiBrowser identified ENO1, an enzyme that catalyzes glycolysis, as a substrate of NEDD4L. Overexpression of NEDD4L resulted in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of ENO1 whereas overexpression of ENO1 reversed the functional effects of NEDD4L overexpression, restoring proliferation, cell cycle transition, and glycolysis in OSCC cells. NEDD4L elicits tumor-suppressive functions via inhibition of OSCC cell proliferation, cell cycle transition, and glycolysis by stimulating ENO1 ubiquitination and degradation. Our results unraveled a signaling axis important for OSCC cell survival and metabolism, which can serve as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Cell cycle; ENO1; glycolysis; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
