Niabella beijingensis sp. nov. and Thermomonas beijingensis sp. nov., two bacteria from constructed wetland
- PMID: 35316171
- PMCID: PMC9558575
- DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.005280
Niabella beijingensis sp. nov. and Thermomonas beijingensis sp. nov., two bacteria from constructed wetland
Abstract
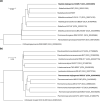
Two Gram-stain-negative, aerobic, non-motile and rod-shaped bacterial strains designated 3A5MI-3T and RSS-23T were isolated from the Dragon-shaped Wetland System in Beijing Olympic Park, PR China. Strain 3A5MI-3T grew at 15–45 °C, pH 5.0–9.0 and with 0–2 % NaCl (w/v), and strain RSS-23T grew at 15-40 oC, pH 5.5–9.0 and with 0–1 % NaCl (w/v). Phylogenetic analyses of 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that strains 3A5MI-3T and RSS-23T were members of
Keywords: CGMCC 1.17737T=KCTC 82817T; CGMCC 1.17738T=KCTC 82820T; Niabella beijingensis sp. nov.; Thermomonas beijingensis sp. nov.; strain 3A5MI-3T; strain RSS-23T.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thermomonas carbonis sp. nov., isolated from the soil of a coal mine.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014 Nov;64(Pt 11):3631-3635. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.063800-0. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25070215
-
Thermomonas flagellata sp. nov. and Thermomonas alba sp. nov., two novel members of the phylum Pseudomonadota isolated from hot spring sediments.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2022 Jun;72(6). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.005444. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35749290
-
Bosea beijingensis sp. nov., Telluria beijingensis sp. nov. and Agrococcus beijingensis sp. nov., isolated from baijiu mash.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024 Mar;74(3). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006304. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38530339
-
Thermomonas koreensis sp. nov., a mesophilic bacterium isolated from a ginseng field.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006 Jul;56(Pt 7):1615-1619. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64049-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16825638
-
Niabella hibiscisoli sp. nov., isolated from soil of a Rose of Sharon garden.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017 Apr;67(4):784-788. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001595. Epub 2017 May 5. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27902198
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

