The oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism rs2268491 and serum oxytocin alterations are indicative of autism spectrum disorder: A case-control paediatric study in Iraq with personalized medicine implications
- PMID: 35316293
- PMCID: PMC8939799
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265217
The oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism rs2268491 and serum oxytocin alterations are indicative of autism spectrum disorder: A case-control paediatric study in Iraq with personalized medicine implications
Abstract
Background: Impairment of social functioning skills is a key hallmark of autism. The neuropeptide oxytocin (OXT) is a blood-based biomarker of social functioning, and a candidate for individualized treatment of ASD. The effects of OXT on the social brain are mediated by the OXT receptor (OXTR). This study assessed the clinical utility of blood OXT serum levels and the OXT receptor (OXTR) genotype as biomarkers of autism and its severity in a pediatric population in Iraq.
Methods: Blood samples were collected from patients with a clinical diagnosis of ASD (n = 60) and corresponding age and gender matched healthy controls (n = 60). All clinical samples were processed at the Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Kufa in Iraq. Blood serum was assayed for OXT by sandwich ELISA. Receiver operator analysis (ROC) determined area under the curve (AUC), cutoff values, and sensitivity and specificity of OXT values for accuracy of diagnosis of ASD. Isolated genomic DNA was genotyped for the OXTR gene rs2268491(C/T) SNP using allele-specific PCR. The significance of genotype (CC, CT, and TT) and allele (C and T) distributions in different patient groups was assessed using odd ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and the Chi-square test. All statistical analysis was performed used SPSS software.
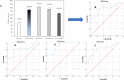
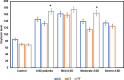
Results: Study characteristics in the ASD population revealed a high level of consanguinity (36.66%), and ASD recurrence rate (11.66%) and family history (28.33%). OXT levels in patients with ASD (157.58±28.81 pg/ml) were significantly higher (p = 0.003) compared to controls (75.03±6.38 pg/ml). Within stratified ASD severity groups-OXT levels were significantly different (P = 0.032). ROC analysis determined similar AUC values for overall ASD (0.807), and stratified mild (0.793), moderate (0.889), and severe categories (0.795). The best cutoff for diagnosis of ASD was 83.8 pg/ml OXT with a sensitivity and specificity of 80% and 72.1% respectively. OXTR gene rs2268491(C/T) genotyping found that ASD patients have significantly lower (p = 0.021) genotype CC frequency and a significantly higher (p = 0.04) occurrence of the heterozygous CT genotype relative to controls. ASD subjects produced highest OXT levels with the TT genotype. T allele distribution was higher in ASD males. ASD males had significantly lower distribution of the CC genotype (48.89%) compared to females (80%) (Chi-square test: χ2 = 4.43, df = 1, p = 0.035). Whereas distribution of the CT genotype was significantly higher in autistic males (44.45%) compared to females (13.33%) (Chi-square test: χ2 = 4.68, df = 1, p = 0.03).
Conclusion: Peripheral OXT levels and OXTR genetic alterations are potential biomarkers of social functioning in the ASD patient setting. The stratification of patients with ASD into severity categories shows significant differences both in OXT levels and OXTR (rs2268491, C/T) genotype and allele distributions, that can be sex dependent. OXT based therapies will require personalized medicine tactics to correctly identify patients with ASD who require neuropeptide boosting in social settings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma oxytocin concentrations and OXTR polymorphisms predict social impairments in children with and without autism spectrum disorder.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 19;111(33):12258-63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402236111. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25092315 Free PMC article.
-
The oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) is associated with autism spectrum disorder: a meta-analysis.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 May;20(5):640-6. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.77. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25092245 Review.
-
Biomarker discovery for disease status and symptom severity in children with autism.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018 Mar;89:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.12.022. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2018. PMID: 29309996 Free PMC article.
-
SNP-PCR genotyping links alterations in the GABAA receptor (GABRG3: rs208129) and RELN (rs73670) genes to autism spectrum disorder among peadiatric Iraqi Arabs.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6019-6028. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07388-z. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35403940 Free PMC article.
-
The role of oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) DNA methylation (DNAm) in human social and emotional functioning: a systematic narrative review.BMC Psychiatry. 2018 May 29;18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1740-9. BMC Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29843655 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A comparison between children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders and healthy controls in biomedical factors, trace elements, and microbiota biomarkers: a meta-analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 9;14:1318637. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1318637. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38283894 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Oxytocin in Pediatric Populations: Exploring the Potential for Reducing Irritability and Modulating Neural Responses: A Mini Review.J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2023;8(4):e230008. doi: 10.20900/jpbs.20230008. Epub 2023 Aug 31. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37990750 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging Genetic Insights with Neuroimaging in Autism Spectrum Disorder-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4938. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094938. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732157 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

