Research Progress of Cell Membrane Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy
- PMID: 35316443
- PMCID: PMC8941025
- DOI: 10.1186/s11671-022-03673-9
Research Progress of Cell Membrane Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy
Abstract
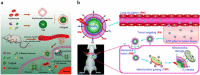
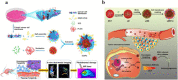
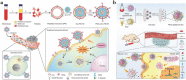
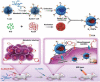
Nanoparticles have unique properties and high design flexibility, which are thought to be safe, site-specific, and efficient drug delivery systems. However, nanoparticles as exogenous materials can provide recognition and be eliminated by the body's immune system, which considerably restricts their applications. To overcome these drawbacks, natural cell membrane coating method has attracted great attention in the field of drug delivery systems, which can prolong nanoparticles blood circulation time and avoiding the capture as well as elimination by the body immune system. Biomimetic nanoparticles via a top-down approach can avoid the laborious group modified engineering and keep the integrity of cell membrane structure and membrane antigens, which can be endowed with unique properties, such as immune escape, longer blood circulation time, targeting delivery and controlling drugs sustain-release. At the present research, erythrocyte membrane, cancer cell membrane, platelet membrane, lymphocyte membrane and hybrid membrane have been successfully coated into the surface of nanoparticles to achieve biological camouflage. Thus, integrating various kinds of cell membranes and nanoparticles into one system, the biomimetic nanoparticles can inherit unique biofunction and drug delivery properties to exhibit tumor targeting-delivery and antitumor outcomes. In this article, we will discuss the prospects and challenges of some basic cell membrane cloaking nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Biomimetic nanoparticles; Cell membrane; Tumor therapy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hybrid cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: A multifunctional biomimetic platform for cancer diagnosis and therapy.Acta Biomater. 2020 Aug;112:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.028. Epub 2020 May 26. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32470527 Review.
-
Oxygen self-enriched nanoparticles functionalized with erythrocyte membranes for long circulation and enhanced phototherapy.Acta Biomater. 2017 Sep 1;59:269-282. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.06.035. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28663143
-
Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: a novel multifunctional biomimetic drug delivery system.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Mar;13(3):716-737. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01252-0. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36417162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of Biomimetic-Responsive Nanocarriers and their Applications in Tumor Targeting.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(12):2255-2273. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220106105315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34994336
-
Coating nanoparticles with cell membranes for targeted drug delivery.J Drug Target. 2015;23(7-8):619-26. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2015.1052074. J Drug Target. 2015. PMID: 26453159 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomimetic Nanomaterials: Diversity, Technology, and Biomedical Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;12(14):2485. doi: 10.3390/nano12142485. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Boron Nitride Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery and Enhanced Antitumor Activity.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 18;15(4):1269. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041269. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111754 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Membrane-Coated TPCS2a-Loaded Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer Photodynamic Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 4;15(6):1654. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061654. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376102 Free PMC article.
-
Erythrocyte-Cancer Hybrid Membrane-Camouflaged Prussian Blue Nanoparticles with Enhanced Photothermal Therapy in Tumors.ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 9;8(25):23056-23066. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02370. eCollection 2023 Jun 27. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37396272 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies and Recent Advances on Improving Efficient Antitumor of Lenvatinib Based on Nanoparticle Delivery System.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jun 10;19:5581-5603. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S460844. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38882543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jelinkovaa P, Mazumdar A, et al. Nanoparticle-drug conjugates treating bacterial infections. J Control Release. 2019;307:166–185. - PubMed
-
- Ding B, Zheng P, et al. MnOx nanospikes as nanoadjuvants and immunogenic cell death drugs with enhanced antitumor immunity and antimetastatic effect. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2020;59:16381–16384. - PubMed
-
- Wan S-S, Cheng Q, et al. A Mn(III)-sealed metal−organic framework nanosystem for redox-unlocked tumor theranostics. ACS Nano. 2019;13:6561–6571. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

