COVID-19 microthrombosis: unusually large VWF multimers are a platform for activation of the alternative complement pathway under cytokine storm
- PMID: 35316498
- PMCID: PMC8938647
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-022-03324-w
COVID-19 microthrombosis: unusually large VWF multimers are a platform for activation of the alternative complement pathway under cytokine storm
Abstract
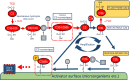
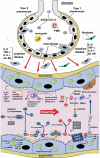
ADAMTS13, a metalloproteinase, specifically cleaves unusually large multimers of von Willebrand factor (VWF), newly released from vascular endothelial cells. The ratio of ADAMTS13 activity to VWF antigen (ADAMTS13/VWF) and indicators of the alternative complement pathway (C3a and sC5b-9) are both related to the severity of COVID-19. The ADAMTS13/VWF ratio is generally moderately decreased (0.18-0.35) in patients with severe COVID-19. When these patients experience cytokine storms, both interleukin-8 and TNFα stimulate VWF release from vascular endothelial cells, while interleukin-6 inhibits both production of ADAMTS13 and its interaction with VWF, resulting in localized severe deficiency of ADAMTS13 activity. Platelet factor 4 and thrombospondin-1, both released upon platelet activation, bind to the VWF-A2 domain and enhance the blockade of ADAMTS13 function. Thus, the released unusually-large VWF multimers remain associated with the vascular endothelial cell surface, via anchoring with syndecan-1 in the glycocalyx. Unfolding of the VWF-A2 domain, which has high sequence homology with complement factor B, allows the domain to bind to activated complement C3b, providing a platform for complement activation of the alternative pathway. The resultant C3a and C5a generate tissue factor-rich neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which induce the mixed immunothrombosis, fibrin clots and platelet aggregates typically seen in patients with severe COVID-19.
Keywords: ADAMTS13; COVID-19; Complement activation; Endotheliopathy; Microthrombosis; VWF.
© 2022. Japanese Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
YF is a recipient of patent royalty for ADAMTS13 activity-ELISA from Alfresa Co. and has received consulting fees from Kainos Co. and Alexion Inc. He also serves as a senior scientist of Japanese Red Cross Kinki Block Blood Center. LZH declares no conflicts of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between the von Willebrand Factor-ADAMTS13 Axis, Complement Activation, and COVID-19 Severity and Mortality.Thromb Haemost. 2022 Feb;122(2):240-256. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1740182. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35062036 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Multimeric von Willebrand Factor and Complement: A Fresh Look to the Pathophysiology of Microvascular Thrombosis.J Immunol. 2017 Aug 1;199(3):1021-1040. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601121. Epub 2017 Jun 26. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28652401
-
Insights Into Immunothrombosis: The Interplay Among Neutrophil Extracellular Trap, von Willebrand Factor, and ADAMTS13.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 2;11:610696. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610696. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33343584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Von Willebrand factor collagen-binding capacity predicts in-hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients: insight from VWF/ADAMTS13 ratio imbalance.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):407-411. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09789-3. Epub 2021 May 11. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33974165 Free PMC article.
-
Update on ADAMTS13 and VWF in cardiovascular and hematological disorders.Clin Chim Acta. 2016 Dec 1;463:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.10.017. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Clin Chim Acta. 2016. PMID: 27746209 Review.
Cited by
-
A predominately pulmonary activation of complement in a mouse model of severe COVID-19.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 3:2024.05.31.596892. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.31.596892. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895461 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Determination of vWF, ADAMTS-13 and Thrombospondin-1 in Venous Thromboembolism and Relating Them to the Presence of Factor V Leiden Mutation.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2024 Jan-Dec;30:10760296231223195. doi: 10.1177/10760296231223195. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2024. PMID: 38225166 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Pattern of Platelet Activation/Reactivity After SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 24;26(1):49. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010049. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement and COVID-19: Three years on, what we know, what we don't know, and what we ought to know.Immunobiology. 2023 May;228(3):152393. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2023.152393. Epub 2023 May 11. Immunobiology. 2023. PMID: 37187043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement is primarily activated in the lung in a mouse model of severe COVID-19.iScience. 2025 Feb 1;28(3):111930. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.111930. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40034849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Menter T, Haslbauer JD, Nienhold R, Savic S, Hopfer H, Deigendesch N, et al. Postmortem examination of COVID-19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings in lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology. 2020;2:198–209. doi: 10.1111/his.14134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

