Decentering predicts attenuated perseverative thought and internalizing symptoms following stress exposure: A multi-level, multi-wave study
- PMID: 35316616
- PMCID: PMC9007852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brat.2021.104017
Decentering predicts attenuated perseverative thought and internalizing symptoms following stress exposure: A multi-level, multi-wave study
Abstract
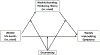
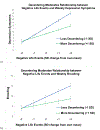
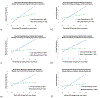
While research identifies a growing list of risk factors for anxiety and depression, it is equally important to identify potential protective factors that may prevent or reduce vulnerability to developing internalizing psychopathology. We hypothesized that forms of perseverative thinking, such as rumination and worry, act as mechanisms linking negative life experiences and prospective symptoms of anxiety and depression. More specifically, we investigated whether decentering, the meta-cognitive capacity to adopt a distanced perspective toward one's thoughts and feelings, serves as a protective factor at various points along this mediational pathway. A sample of 181 undergraduate students were recruited and assessed at five time points over a 12-week period. Multilevel modeling indicated that decentering was associated with an attenuated impact of (1) negative events on prospective depressive symptoms; (2) negative events on prospective brooding, and (3) brooding, pondering and worry on prospective internalizing symptoms. Multilevel moderated mediation analyses provided partial support for the hypothesis that perseverative thinking would mediate the longitudinal associations between negative life events and internalizing symptoms, with decentering attenuating risk at several connections of the indirect pathways. The strongest support was provided for moderated mediation models in which decentering was associated with attenuated relationships between negative events, brooding, and symptoms of depression. This study is the first to elucidate the role of decentering as a protective factor against anxiety and depressive symptoms at different points in the path from stress to perseverative thought to internalizing symptoms. Decentering therefore may be a critical target for clinical intervention to promote resilience against anxiety and depression.
Keywords: Anxiety; Decentering; Depression; Perseverative thinking; Rumination; Stress; Worry.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Worry and Rumination Specific Pathways Linking Neuroticism and Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Major Depressive Disorder and Mixed Anxiety-Depressive Disorder?PLoS One. 2016 May 31;11(5):e0156169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156169. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27243462 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Relations of Worry, Rumination, and Psychopathology Symptoms After Loss: A Prospective Cohort Study.Behav Ther. 2022 Sep;53(5):793-806. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2022.01.001. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Behav Ther. 2022. PMID: 35987539
-
Rumination as a mechanism linking stressful life events to symptoms of depression and anxiety: longitudinal evidence in early adolescents and adults.J Abnorm Psychol. 2013 May;122(2):339-52. doi: 10.1037/a0031994. J Abnorm Psychol. 2013. PMID: 23713497 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive negative thinking as a mediator in prospective cross-disorder associations between anxiety and depression disorders and their symptoms.J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2019 Jun;63:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 29. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30551055
-
Decentering as a core component in the psychological treatment and prevention of youth anxiety and depression: a narrative review and insight report.Transl Psychiatry. 2021 May 14;11(1):288. doi: 10.1038/s41398-021-01397-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33990541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How does mindfulness skills training work to improve emotion dysregulation in borderline personality disorder?Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2024 Sep 2;11(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s40479-024-00265-0. Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. 2024. PMID: 39218933 Free PMC article.
-
Momentary impulsivity interferes with emotion regulation strategy prioritization in everyday life in remitted depression.Behav Res Ther. 2024 Jan;172:104424. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2023.104424. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Behav Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38103360 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Public Risk Familiarity and Mental Health During the COVID-19 Epidemic: A Moderated Mediation Model.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 5;13:945928. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.945928. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35865701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abela JRZ, & Hankin BL (2008). Cognitive vulnerability to depression in children and adolescence: A developmental psychopathology perspective. In Abela JRZ & Hankin BL (Eds.), Handbook of Depression in Children and Adolescents (pp. 35–78). Guilford Press.
-
- Aiken LS, & West SG (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. SAGE.
-
- Alloy LB, Abramson LY, Raniere D, & Dyller IM (1999). Research methods in adult psychopathology. In Kendall PC, Butcher JN, & Holmbeck GN (Eds.), Handbook of research methods in clinical psychology (pp. 466–498). John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

