A phospholipid mimetic targeting LRH-1 ameliorates colitis
- PMID: 35316658
- PMCID: PMC11288311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2022.03.001
A phospholipid mimetic targeting LRH-1 ameliorates colitis
Abstract
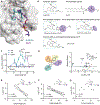
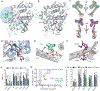
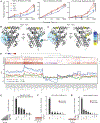
Phospholipids are ligands for nuclear hormone receptors (NRs) that regulate transcriptional programs relevant to normal physiology and disease. Here, we demonstrate that mimicking phospholipid-NR interactions is a robust strategy to improve agonists of liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1), a therapeutic target for colitis. Conventional LRH-1 modulators only partially occupy the binding pocket, leaving vacant a region important for phospholipid binding and allostery. Therefore, we constructed a set of molecules with elements of natural phospholipids appended to a synthetic LRH-1 agonist. We show that the phospholipid-mimicking groups interact with the targeted residues in crystal structures and improve binding affinity, LRH-1 transcriptional activity, and conformational changes at a key allosteric site. The best phospholipid mimetic markedly improves colonic histopathology and disease-related weight loss in a murine T cell transfer model of colitis. This evidence of in vivo efficacy for an LRH-1 modulator in colitis represents a leap forward in agonist development.
Keywords: LRH-1; agonist; coregulator; liver; nuclear receptor; phospholipid; ulcerative colitis; x-ray crystallography.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests E.A.O., S.G.M., A.R.F., and N.T.J. have a patent related to this work.
Figures


References
-
- Aarts JM, Wang S, Houtman R, van Beuningen RM, Westerink WM, Van De Waart BJ, Rietjens IM, and Bovee TF (2013). Robust array-based coregulator binding assay predicting ERalpha-agonist potency and generating binding profiles reflecting ligand structure. Chem Res Toxicol 26, 336–346. - PubMed
-
- Basak O, Beumer J, Wiebrands K, Seno H, van Oudenaarden A, and Clevers H (2017). Induced Quiescence of Lgr5+ Stem Cells in Intestinal Organoids Enables Differentiation of Hormone-Producing Enteroendocrine Cells. Cell Stem Cell 20, 177–190 e174. - PubMed
-
- Bouguen G, Langlois A, Djouina M, Branche J, Koriche D, Dewaeles E, Mongy A, Auwerx J, Colombel JF, Desreumaux P, et al. (2015). Intestinal steroidogenesis controls PPARgamma expression in the colon and is impaired during ulcerative colitis. Gut 64, 901–910. - PubMed

