Microwave Ablation for Malignant Central Airway Obstruction: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 35316812
- PMCID: PMC9393822
- DOI: 10.1159/000522544
Microwave Ablation for Malignant Central Airway Obstruction: A Pilot Study
Abstract
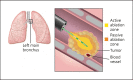
Background: Malignant central airway obstruction (CAO) is a debilitating complication of primary lung cancer and pulmonary metastases. Therapeutic bronchoscopy is used to palliate symptoms and/or bridge to further therapy. Microwave ablation (MWA) heats tissue by creating an electromagnetic field around an ablation device. We present a pilot study utilizing endobronchial MWA via flexible bronchoscopy as a novel modality for the management of malignant CAO.
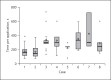
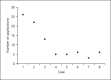
Methods: Therapeutic bronchoscopy with a flexible MWA probe was performed in 8 cases. We reviewed tumor size, previous ablative techniques, number of applications, ablation time, amount of energy delivered, rate of successful recanalization, complications, and 30-day follow-up.
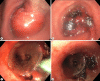
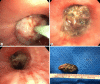
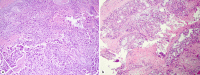
Results: Successful airway recanalization was achieved in all cases. No complications were noted. In 1 case, tumor in-growth within a silicone stent was ablated with no damage to the stent.
Discussion: Endobronchial MWA is a novel technique for tumor destruction while maintaining an airway axis. The oven effect and air gap around a tumor allow for safe and effective tissue devitalization and hemostasis without a thermal effect on structures surrounding the airway.
Keywords: Airway obstruction; Bronchoscopic treatment; Interventional bronchoscopy; Lung cancer; Microwave ablation; Tracheobronchial obstruction; Tumor ablation.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
M.S. has been a scientific consultant for Medtronic Inc., MedWave Inc., and Optellum Inc. G.E.A. has been a scientific consultant for AstraZeneca. E.F. has been a scientific consultant for Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Cook. E.F. has received an institutional grant from Intuitive Surgical. C.L.O., W.B.H., and I.A. have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bronchoscopic Ablative Therapies for Malignant Central Airway Obstruction and Peripheral Lung Tumors.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 Oct;16(10):1220-1229. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201812-892CME. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019. PMID: 31194922 Review.
-
Impact of Silicone Stent Placement in Symptomatic Airway Obstruction due to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer - A French Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study: The SPOC Trial.Respiration. 2020;99(4):344-352. doi: 10.1159/000506601. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Respiration. 2020. PMID: 32213777 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and effectiveness of microdebrider bronchoscopy for the management of central airway obstruction.Respirology. 2013 Aug;18(6):1011-5. doi: 10.1111/resp.12087. Respirology. 2013. PMID: 23520982
-
[Bronchoscopic treatment of malignant central airway obstruction: A cohort study, long-term survival and complications].Rev Mal Respir. 2022 Jun;39(6):505-515. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2022.04.004. Epub 2022 May 17. Rev Mal Respir. 2022. PMID: 35589481 French.
-
[Present status of interventional pulmonology].Kyobu Geka. 2014 Jul;67(8):710-4. Kyobu Geka. 2014. PMID: 25138943 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the efficacy and adverse events between argon-helium cryoablation and microwave ablation for non-small cell lung cancer: a propensity score matching study.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Jul 31;17(7):4587-4599. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2024-2228. Epub 2025 Jul 22. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40809279 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of malignant central airway obstruction.Mediastinum. 2023 Jul 11;7:32. doi: 10.21037/med-22-44. eCollection 2023. Mediastinum. 2023. PMID: 38090036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of different temperatures on chondrocyte growth: a transcriptomic analysis.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Dec 20;17(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-02070-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39707345 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional bronchoscopy in lung cancer treatment.Breathe (Sheff). 2024 Aug 27;20(2):230201. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0201-2023. eCollection 2024 Jun. Breathe (Sheff). 2024. PMID: 39193456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
All-in-one properties of an anticancer-covered airway stent for the prevention of malignant central airway obstruction.APL Bioeng. 2023 Sep 13;7(3):036116. doi: 10.1063/5.0157341. eCollection 2023 Sep. APL Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 37719298 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ernst A, Feller-Kopman D, Becker HD, Mehta AC. Central airway obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169((12)):1278–97. - PubMed
-
- Oberg C, Folch E, Santacruz JF. Management of malignant airway obstruction. AME Med J. 2018 Dec 18;3:115.
-
- Mahmood K, Wahidi MM, Thomas S, Argento AC, Ninan NA, Smathers EC, et al. Therapeutic bronchoscopy improves spirometry, quality of life, and survival in central airway obstruction. Respiration. 2015;89((5)):404–13. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan AK, Ibrahim O, Perez R, Oberg CL, Majid A, Folch E. Electrosurgical and laser therapy tools for the treatment of malignant central airway obstructions. Chest. 2020 Feb;157((2)):446–53. - PubMed
-
- Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW. Microwave ablation: principles and applications. Radiographics. 2005;25((Suppl 1)):S69–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

