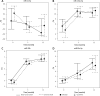
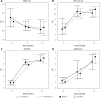
Twelve-month kinetics of circulating fibrosis-linked microRNAs (miR-21, miR-29, miR-30, and miR-133a) and the relationship with extracellular matrix fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 35316894
- PMCID: PMC8924829
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2019.89777
Twelve-month kinetics of circulating fibrosis-linked microRNAs (miR-21, miR-29, miR-30, and miR-133a) and the relationship with extracellular matrix fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Introduction: A single measurement of any biomarker may not reflect its full biological meaning. The kinetics of fibrosis-linked microRNAs and their relationship with extracellular matrix (ECM) fibrosis in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) have not been explored.
Material and methods: We evaluated 70 consecutive DCM patients (48 ±12.1 years, left ventricular ejection fraction 24.4 ±7.4%). All patients underwent right ventricular endomyocardial biopsy in order to quantify ECM fibrosis and measure collagen volume fraction (CVF). Circulating microRNAs (miR-21-5p, miR-29b, miR-30c-5p, and miR-133a-3p) were measured with quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) at baseline and at 3 and 12 months.
Results: Based on the biopsy results, two groups of patients were identified: with (n = 24, 34.3%) and without (n = 46, 65.7%) ECM fibrosis. Except for a single measurement of miR-29b at 3 months (DCM with fibrosis: 6.03 ±0.72 vs. DCM without fibrosis: 6.4 ±0.75 ΔCq; p < 0.05), baseline, 3- and 12-month kinetics of microRNAs did not differ between the two groups. Moreover, 12-month microRNA kinetics did not differ in patients with new-onset DCM (duration < 6 months; n = 35) and chronic DCM (> 6 months; n = 35). Only miR-29 at 3 months correlated with CVF (r = -0.31; p < 0.05), whereas other microRNAs did not correlate with CVF either at 3 or at 12 months.
Conclusions: Regardless of ECM fibrosis status or duration of the disease, 12-month patterns of circulating microRNAs are similar in DCM. Correlations between microRNAs, measured at 3 and 12 months, are lower than expected. In this study, regardless of the time point, circulating microRNAs were not able to differentiate between DCM patients with versus without fibrosis.
Keywords: cardiomyopathy; fibrosis; kinetics; microRNA.
Copyright: © 2019 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between myocardial fibrosis and myocardial microRNAs in dilated cardiomyopathy: A link between mir-133a and cardiovascular events.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2514-2517. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13535. Epub 2018 Jan 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29377565 Free PMC article.
-
Relations between circulating and myocardial fibrosis-linked microRNAs with left ventricular reverse remodeling in dilated cardiomyopathy.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 Mar;29(3):285-293. doi: 10.17219/acem/115088. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32207584
-
Right ventricular morphology and function is not related with microRNAs and fibrosis markers in dilated cardiomyopathy.Cardiol J. 2018;25(6):722-731. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2017.0099. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Cardiol J. 2018. PMID: 28840590
-
Characteristic adaptations of the extracellular matrix in dilated cardiomyopathy.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Oct 1;220:634-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.06.253. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27391006 Review.
-
MicroRNA targets and biomarker validation for diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105941. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105941. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34656765 Review.
Cited by
-
Atrial Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanistic Insights, Diagnostic Challenges, and Emerging Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 30;26(1):209. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010209. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translation of pathophysiological mechanisms of atrial fibrosis into new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025 Apr;22(4):225-240. doi: 10.1038/s41569-024-01088-w. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39443702 Review.
-
Association between Circulating MicroRNAs (miR-21-5p, miR-20a-5p, miR-29b-3p, miR-126-3p and miR-101-3p) and Chronic Allograft Dysfunction in Renal Transplant Recipients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 14;23(20):12253. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012253. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293110 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetes: Pathogenesis and Targeted Rhythm Control Strategies.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 17;47(7):559. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070559. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40729028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Czarkowska-Pączek B, Czek B, Przybylski J, et al. Proteolytic enzymes activities in patients after myocardial infarction correlate with serum concentration of TGF-beta. Inflammation. 2004;28:279–84. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources