Nasal bone to nasal tip length ratio for describing nasal bone hypoplasia and predicting trisomy 21
- PMID: 35316896
- PMCID: PMC8924847
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2019.85655
Nasal bone to nasal tip length ratio for describing nasal bone hypoplasia and predicting trisomy 21
Abstract
Introduction: Fetal nasal bone hypoplasia has been proven to be a strong marker for trisomy 21 during second trimester ultrasonography. Rather than evaluating the nasal bone hypoplasia according to the nomograms, it may be possible to evaluate it with a more practical and specific method.
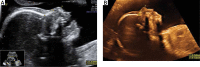
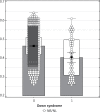
Material and methods: Retrospectively collected data were provided from the saved and stored patient data between 2012 and 2017. Nasal bone length and nasal tip length were measured and the ratio was calculated. The ratio ≤ 1/3 was defined as the threshold ratio for the definition of the marker. Nasal bone nasal tip length (NB/NL) ratio values were compared among groups with trisomy 21 and euploid fetuses.
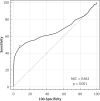
Results: A total of 59 fetuses had trisomy 21 and 2304 euploid fetuses were included in the study. The ratio of nasal bone to nasal tip length was 1/3 and below in 21/59 (35.5%) of fetuses with trisomy 21 whereas this ratio was 31/2304 (1.3%) in euploid fetuses. The difference was statistically significant (p < 0.001). Sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio of nasal bone/nasal tip ratio ≤ 1/3 were 35.5%, 98.6%, 26.4 and 0.6 for Down syndrome, respectively.
Conclusions: This study suggested that the nasal bone to nasal tip length ratio may be a new promising and practical sonographic marker in the second trimester genetic sonography. Although its sensitivity is not high, it seems to be more practical and specific than the evaluation of fetal nasal bone length.
Keywords: Down syndrome; nasal bone hypoplasia; nasal tip length; prenatal diagnosis.
Copyright: © 2019 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fetal nasal bone and trisomy 21 in the second trimester.Prenat Diagn. 2005 Jun;25(6):511-5. doi: 10.1002/pd.848. Prenat Diagn. 2005. PMID: 15968623
-
Assessing the value of second-trimester nasal bone hypoplasia in predicting chromosomal abnormalities: a retrospective chromosomal microarray analysis of 351 fetuses.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023 Oct;308(4):1263-1270. doi: 10.1007/s00404-022-06808-6. Epub 2022 Oct 21. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2023. PMID: 36269386
-
Normal Range of Fetal Nasal Bone Length during the Second Trimester in an Afro-Caribbean Population and Likelihood Ratio for Trisomy 21 of Absent or Hypoplastic Nasal Bone.Fetal Diagn Ther. 2017;42(2):130-136. doi: 10.1159/000450996. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2017. PMID: 27764826
-
Nasal bone assessment in prenatal screening for trisomy 21.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006 Nov;195(5):1219-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2005.11.042. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006. PMID: 16615922 Review.
-
Nuchal translucency and other first-trimester sonographic markers of chromosomal abnormalities.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004 Jul;191(1):45-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.03.090. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004. PMID: 15295343 Review.
Cited by
-
Reference values for ductus venosus Doppler velocity indices between 11 and 13+6 weeks of gestation: A single-center prospective study in Iran.J Res Med Sci. 2023 Jun 28;28:55. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_808_22. eCollection 2023. J Res Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37496642 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Fetal Anomaly Detection in Ultrasonography Images: A Review of Machine Learning-Based Approaches.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;8(7):519. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8070519. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999160 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cicero S, Curcio P, Papageorghiou A, Sonek J, Nicolaides K. Absence of nasal bone in fetuses with trisomy 21 at 11–14 weeks of gestation: an observational study. Lancet. 2001;358:1665–7. - PubMed
-
- Cusick W, Provenzano J, Sullivan CA, Gallousis FM, Rodis JF. Fetal nasal bone length in euploid and aneuploid fetuses between 11 and 20 weeks’ gestation. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23:1327–33. - PubMed
-
- Odibo AO, Sehdev HM, Dunn L, McDonald R, Macones GA. The association between fetal nasal bone hypoplasia and aneuploidy. Obstetrics Gynecol. 2004;104:1229–33. - PubMed
-
- Viora E, Errante G, Sciarrone A, et al. Fetal nasal bone and trisomy 21 in the second trimester. Prenatal Diagnosis. 2005;25:511–5. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Cid M, Rubio-Lorente A, Rodriguez M, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of performance of second-trimester nasal bone assessment in detection of fetuses with Down syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014;43:247–53. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
