Omega-6 fatty acids and the risk of cardiovascular disease: insights from a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and a Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 35316920
- PMCID: PMC8924827
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms/136070
Omega-6 fatty acids and the risk of cardiovascular disease: insights from a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and a Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
Introduction: Omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) represent almost 15% of the total energy intake in Western countries. Their effects on the cardiovascular (CV) risk factors are still controversial. Thus, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials (RCTs) as well as a Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to evaluate the links and possible causality between supplementation or serum levels of omega-6 PUFA, CV disease (CVD) and cardiometabolic risk factors.
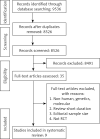
Material and methods: Selected databases were searched until September 2019 to identify prospective studies investigating the effects of omega-6 PUFA supplementation on CVD events/mortality. Random-effects model meta-analysis was performed for quantitative data synthesis. Trial sequential analysis (TSA) was used to evaluate the optimal sample size to detect a 20% reduction in outcomes after administration of omega-6 PUFAs. The inverse variance weighted (IVW) method, weighted median-based method, MR-Egger and MR-Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier (PRESSO) were applied for MR.
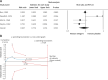
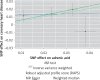
Results: The pooled estimate risk ratio (RR) of omega-6 PUFA supplementation was 0.94 for any CVD event (95% CI: 0.77-1.15, I 2 = 66.2%), 1.06 for CVD death (95% CI: 0.73-1.55, I 2 = 66.2%), 0.84 for coronary heart disease (CHD) events (95% CI: 0.61-1.16, I 2 = 79.4%), 0.87 for myocardial infarction (MI) (95% CI: 0.74-1.01, I 2 = 2.3%) and 1.36 for stroke (95% CI: 0.45-4.07, I 2 = 55.3%). In contrast, MR showed that individuals with higher serum omega-6 acid - adrenic acid (AA) levels had a greater risk for CHD events (IVW β = 0.526), MI (IVW β = 0.606) and large artery stroke (IVW β = 1.694), as well as increased levels of fasting blood glucose (FBG) (IVW β = 0.417), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (IVW β = 0.806), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (IVW β = 0.820), and lower levels of triglycerides (TG) (IVW β = -1.064) and total cholesterol (TC) (IVW β = -1.064).
Conclusions: Omega-6 PUFA supplementation did not affect the risk for CVD morbidity and mortality. Additionally, based on MR analysis we found that higher AA levels might even significantly increase the risk of CHD, MI and large artery stroke, as well as the levels of FBG and LDL-C, whereas they were negatively associated with TC and TG. Since a considerable chance of heterogeneity was observed for some of the results, further research is needed to elucidate the effects of omega-6 PUFAs on cardiometabolic outcomes.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular mortality; coronary heart disease; meta-analysis; omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids; stroke.
Copyright: © 2022 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
NK has given talks, attended conferences and participated in trials sponsored by Angelini, Astra Zeneca, Bausch Health, Boehringer Ingelheim, Elpen, Mylan, NovoNordisk, Sanofi and Servier. All other authors have nothing to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Begg S, Vos T, Barker B, Stevenson C, Stanley L, Lopez AD. The burden of disease and injury in Australia 2003. PHE 82. Canberra: AIHW; 2007.
-
- Harris WS, Mozaffarian D, Rimm E, et al. Omega-6 fatty acids and risk for cardiovascular disease: a science advisory from the American Heart Association Nutrition Subcommittee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism; Council on Cardiovascular Nursing; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2009;119:902–7. - PubMed
-
- Russo GL. Dietary n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: from biochemistry to clinical implications in cardiovascular prevention. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:937–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
