Screening of stable resistant accessions and identification of resistance loci to Barley yellow mosaic virus disease
- PMID: 35317071
- PMCID: PMC8934529
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13128
Screening of stable resistant accessions and identification of resistance loci to Barley yellow mosaic virus disease
Abstract
Background: The disease caused by Barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV) infection is a serious threat to autumn-sown barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) production in Europe, East Asia and Iran. Due to the rapid diversification of BaYMV strains, it is urgent to discover novel germplasm and genes to assist breeding new varieties with resistance to different BaYMV strains, thus minimizing the effect of BaYMV disease on barley cropping.
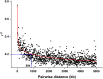
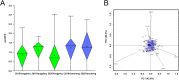
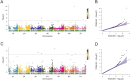
Methods: A natural population consisting of 181 barley accessions with different levels of resistance to BaYMV disease was selected for field resistance identification in two separate locations (Yangzhou and Yancheng, Jiangsu Province, China). Additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI) analysis was used to identify accessions with stable resistance. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) of BaYMV disease resistance was broadly performed by combining both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and specific molecular markers associated with the reported BaYMV disease resistance genes. Furthermore, the viral protein genome linked (VPg) sequences of the virus were amplified and analyzed to assess the differences between the BaYMV strains sourced from the different experimental sites.
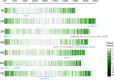
Results: Seven barley accessions with lower standardized Area Under the Disease Progress Steps (sAUDPS) index in every environment were identified and shown to have stable resistance to BaYMV disease in each assessed location. Apart from the reported BaYMV disease resistance genes rym4 and rym5, one novel resistance locus explaining 24.21% of the phenotypic variation was identified at the Yangzhou testing site, while two other novel resistance loci that contributed 19.23% and 19.79% of the phenotypic variation were identified at the Yancheng testing site, respectively. Further analysis regarding the difference in the VPg sequence of the predominant strain of BaYMV collected from these two testing sites may explain the difference of resistance loci differentially identified under geographically distinct regions. Our research provides novel genetic resources and resistance loci for breeding barley varieties for BaMYV disease resistance.
Keywords: Additive main effects and multiplicative interaction (AMMI); Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.); Barley yellow mosaic disease (BYMD); Genome-wide association study (GWAS); Stable resistant accessions.
© 2022 Pan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of novel QTL contributing to barley yellow mosaic resistance in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare spp. spontaneum).BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Nov 25;21(1):560. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03321-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 34823470 Free PMC article.
-
Bulked segregant RNA-sequencing (BSR-seq) identified a novel rare allele of eIF4E effective against multiple isolates of BaYMV/BaMMV.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 Jun;132(6):1777-1788. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03314-3. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30815718
-
High-resolution mapping of the Rym4/Rym5 locus conferring resistance to the barley yellow mosaic virus complex (BaMMV, BaYMV, BaYMV-2) in barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. vulgare L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2005 Jan;110(2):283-93. doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1832-4. Epub 2004 Nov 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2005. PMID: 15551112
-
Molecular markers in breeding for virus resistance in barley.J Appl Genet. 2004;45(2):145-59. J Appl Genet. 2004. PMID: 15131346 Review.
-
Bymovirus-induced yellow mosaic diseases in barley and wheat: viruses, genetic resistances and functional aspects.Theor Appl Genet. 2020 May;133(5):1623-1640. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03555-7. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Theor Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32008056 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association studies reveal stable loci for wheat grain size under different sowing dates.PeerJ. 2024 Feb 26;12:e16984. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16984. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38426132 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association scan and transcriptome analysis reveal candidate genes for waterlogging tolerance in cultivated barley.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Dec 15;13:1048939. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1048939. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36589094 Free PMC article.
-
A novel QTL qRYM-7H for barley yellow mosaic resistance identified by GWAS and linkage analysis.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 22;114(6):127. doi: 10.1007/s11103-024-01529-7. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39572425
-
Genome-wide association studies reveal novel loci for grain size in two-rowed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Feb 26;137(3):58. doi: 10.1007/s00122-024-04562-8. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38407646
References
-
- Aguado Eón, García A, Iglesias-Moya J, Romero J, Wehner TC, Gómez-Guillamón M L, Picó B, Garcés-Claver A, Martínez C, Jamilena M. Mapping a Partial Andromonoecy locus in Citrullus lanatus using BSA-Seq and GWAS approaches. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2020;11:1243. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01243. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker BM, Waiker SC. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software. 2015;67(1):1–38. doi: 10.18637/jss.v067.i01. - DOI
-
- Bauer E, Weyen J, Schiemann A, Graner A, Ordon F. Molecular mapping of novel resistance genes against Barley Mild Mosaic Virus (BaMMV) Theoretical Applied Genetics. 1997;95(8):1263–1269. doi: 10.1007/s001220050691. - DOI
-
- Belcher AR, Cuesta-Marcos A, Smith KP, Mundt CC, Chen X, Hayes PM. TCAP FAC-WIN6 elite barley GWAS panel QTL. I. barley stripe rust resistance QTL in facultative and winter six-rowed malt barley breeding programs identified via GWAS. Crop Science. 2018;58(1):103–119. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2017.03.0206. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

