The Interaction Between Non-Coding RNAs and Calcium Binding Proteins
- PMID: 35317077
- PMCID: PMC8934394
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.848376
The Interaction Between Non-Coding RNAs and Calcium Binding Proteins
Abstract
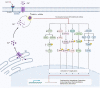
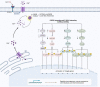
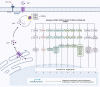
Calcium binding proteins (CBP) are a group of proteins mediating the effects of calcium on cellular functions. These proteins can regulate calcium levels inside the cells and contribute in several cellular functions through transporting this ion across cell membranes or decoding related signals. Recent studies have shown that several non-coding RNAs interact with CBPs to affect their expression or activity. The interactions between these transcripts and CBPs have implications in the pathoetiology of human disorders, including both neoplastic and non-neoplastic conditions. In the current review, we describe the interactions between three classes of non-coding RNAs (long non-coding RNAs, circular RNAs, and microRNAs) and a number of CBPs, particularly CAB39, S100A1, S100A4, S100A7 and S100P. This kind of interaction has been verified in different pathological contexts such as drug-induced cardiotoxicity, osteoblasts cytotoxicity, acute lung injury, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, glomerulonephritis, as well as a wide array of neoplastic conditions.
Keywords: calcium binding protein; circRNA; lncRNA; miRNA; non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2022 Ghafouri-Fard, Majidpoor, Shoorei, Hussen, Hadayat Jamal, Baniahmad, Taheri and Mokhtari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction between SIRT1 and non-coding RNAs in different disorders.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 27;14:1121982. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1121982. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37441551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs on Immune Responses During Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 9;12:798713. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.798713. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34956235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Ischemic Myocardial Reperfusion Injury.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019 Aug;33(4):489-498. doi: 10.1007/s10557-019-06893-x. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019. PMID: 31332654 Review.
-
Emerging Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Senescence.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 5;10:869011. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.869011. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35865636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A transcriptomic profile of topping responsive non-coding RNAs in tobacco roots (Nicotiana tabacum).BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 14;20(1):856. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6236-6. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31726968 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Distinct microRNA and protein profiles of extracellular vesicles secreted from myotubes from morbidly obese donors with type 2 diabetes in response to electrical pulse stimulation.Front Physiol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1143966. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1143966. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37064893 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Roles of Circular RNA in Tumor Metastasis via Acting as a Sponge of miRNA/isomiR.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 24;23(13):7024. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137024. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of expression of calcium signaling related lncRNAs in epilepsy.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 21;13(1):17993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45341-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37865723 Free PMC article.
-
circ_0052184 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression via Targeting miR-604/HOXA9 Axis.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022 Aug 27;2022:8583382. doi: 10.1155/2022/8583382. eCollection 2022. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022. PMID: 36065412 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of S100P in pan carcinoma: Biological functions and mechanisms (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Jun;53(6):62. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8895. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40211698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

