Zerumbone mediates apoptosis and induces secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in breast carcinoma cell culture
- PMID: 35317109
- PMCID: PMC8917841
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.58573.13012
Zerumbone mediates apoptosis and induces secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in breast carcinoma cell culture
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the potential anti-breast cancer activity of zerumbone in regulating apoptotic mediators and cytokines in comparison with paclitaxel (positive control).
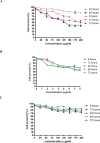
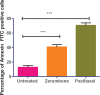
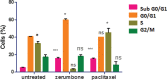
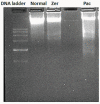
Materials and methods: In this study, assays such as viability, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species, cell cycle, DNA fragmentation, and cytokines were carried out on MCF-7 cells after treatment with zerumbone and paclitaxel.
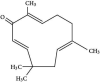
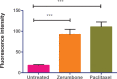
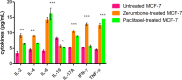
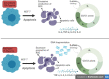
Results: The results showed that zerumbone demonstrated a higher (18-fold) IC50 value (126.7 µg/ml) than paclitaxel (7.29 µg/ml) in order to suppress proliferation and induce cell death of MCF-7. The cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase and excessive intracellular ROS production during the in vitro zerumbone treatment indicated occurrence of apoptotic cell death although nuclear DNA fragmentation was not observed. The flow cytometer analysis of treated cells revealed secretion of proinflammatory cytokines suggesting the potential immunomodulatory activity of zerumbone.
Conclusion: Although, zerumbone exhibited a higher IC50 value compared with paclitaxel yet its anticancer activity against MCF-7 cells is still parallel to paclitaxel hence zerumbone has the potential to be an antineoplastic agent in the treatment of breast cancer especially the luminal type A.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast; Cytokine; Natural; Zerumbone.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no potential conflicts of interest reported by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;0:caac. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
