Mesenchymal stem cells promote caspase-3 expression of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via reducing telomerase activity and telomere length
- PMID: 35317118
- PMCID: PMC8917842
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2021.59400.13187
Mesenchymal stem cells promote caspase-3 expression of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells via reducing telomerase activity and telomere length
Abstract
Objectives: The use of mesenchymal stem cells in malignancies has attracted much attention due to their ability to deliver anticancer agents to tumors, including cytokines, chemokines, etc. This study aimed to investigate the effect of MSCs on the neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells through proliferation/apoptosis, senescence assessment, telomere length, and telomerase activity in vitro. BAX and BCL2 were also examined as potential signaling pathways in this process.
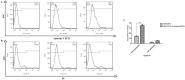
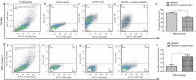
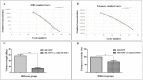
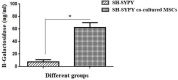
Materials and methods: For this reason, two cell populations (MSCs and SH-SY5Y cells) were co-cultured on trans-well plates for 7 days. In a subsequent step, SH-SY5Y cells were harvested from both control and experimental groups and subjected to flow cytometry, ELISA, real-time PCR, PCR-ELISA TRAP assay, and Western blotting assay for Ki67/Caspase3 investigation, β-Galactosidase assessment, telomere length, and telomerase activity assay. Also, expression of genes and proteins through real-time PCR and Western blotting demonstrated the involvement of the aforementioned signaling pathways in this process.
Results: It was found that MSCs contributed significantly to decrease and increase of Ki-67 and Caspase-3, respectively. Also, MSCs dramatically reduced the length of telomere and telomerase activity and increased the β-Galactosidase activity in a significant manner. In addition, significant increase and decrease were also seen in BAX and BCL2 gene and protein expressions, respectively.
Conclusion: These findings revealed that close interaction between MSCs and neuroblastoma cells causes inhibition of the SH-SY5Y cell proliferation and promotes cell senescence via BAX and caspase-3 cascade pathways.
Keywords: Caspase3; Mesenchymal stem cells; Neuroblastoma; Signaling pathways; Telomerase; Telomere.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6, -8, and TGF-β Secreted from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Show Functional Role in Reduction of Telomerase Activity of Leukemia Cell Via Wnt5a/β-Catenin and P53 Pathways.Adv Pharm Bull. 2020 Jun;10(2):307-314. doi: 10.34172/apb.2020.037. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 32373501 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Caspase Expression in Molt-4 Leukemia Cells Via GSK-3α/Β and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways as a Therapeutic Strategy.Curr Gene Ther. 2021;21(1):81-88. doi: 10.2174/1566523220666201005111126. Curr Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33019931
-
XAV939 promotes apoptosis in a neuroblastoma cell line via telomere shortening.Oncol Rep. 2014 Nov;32(5):1999-2006. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3460. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25190315
-
Impact of Mothers' Age on Telomere Length and Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Expression in Human Fetal Membrane-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2019 Dec 15;28(24):1632-1645. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0144. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Stem Cells Dev. 2019. PMID: 31650883
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells cause Telomere Length Reduction of Molt-4 Cells via Caspase-3, BAD and P53 Apoptotic Pathway.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2021 Spring;10(2):113-122. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.10.2.113. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2021. PMID: 34703795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote osteoblast proliferation, migration and inhibit apoptosis by regulating KLF3-AS1/miR-338-3p.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Feb 9;25(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07236-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38336637 Free PMC article.
-
ERK1-mediated immunomodulation of mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates inflammatory disorders.iScience. 2023 Sep 9;26(10):107868. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107868. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37790278 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation the apoptotic effect of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) on MDA-MB 231 breast cancer epithelial cells via signaling pathways.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 26;10(5):e26959. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26959. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38455550 Free PMC article.
-
miR-642a-5p increases glucocorticoid sensitivity by suppressing the TLR4 signalling pathway in THP-1 cells.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Sep 27;32:101356. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101356. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36186733 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF3IP2 drives mesenchymal stem cell senescence via regulation of NAMPT-mediated NAD biosynthesis.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 29;9(9):e19505. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19505. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matthay KK. Interleukin 2 plus anti-GD2 immunotherapy: helpful or harmful? Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1549–1551. - PubMed
-
- Nakamizo A, Marini F, Amano T, Khan A, Studeny M, Gumin J, et al. Human bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gliomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3307–3318. - PubMed
-
- Fathi E, Farahzadi R. Isolation, culturing, characterization and aging of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a brief overview. Braz Arch Biol Technol. 2016;59:1–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
